Bongkrekic acid
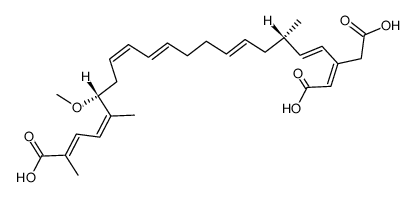
Bongkrekic acid structure
|
Common Name | Bongkrekic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 11076-19-0 | Molecular Weight | 486.59700 | |
| Density | 1.114g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 715.1ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38O7 | Melting Point | 50-60° | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 231ºC | |
Use of Bongkrekic acidBongkrekic acid is a mitochondrial toxin secreted by the bacteria Pseudomonas cocovenenans[1]. Bongkrekic acid specific ligand for mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) rather than the electron transport chain. Bongkrekic acid has to cross the mitochondrial inner membrane to produce its inhibitory effect on ADP/ATP transport[2]. |
| Name | bongkrekic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bongkrekic acid is a mitochondrial toxin secreted by the bacteria Pseudomonas cocovenenans[1]. Bongkrekic acid specific ligand for mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) rather than the electron transport chain. Bongkrekic acid has to cross the mitochondrial inner membrane to produce its inhibitory effect on ADP/ATP transport[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Bongkrekic acid (0-50 μM; 48 hours) stimulated formazan formation in MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 and LTED cells with EC50 of 34.14 μM, >50 μM and 2.58 μM, respectively. Bongkrekic acid (0.1-25 μM; 48 hours) decreases the living cell numbers in LTED cells and parent MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.114g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 715.1ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 50-60° |
| Molecular Formula | C28H38O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 486.59700 |
| Flash Point | 231ºC |
| Exact Mass | 486.26200 |
| PSA | 121.13000 |
| LogP | 5.88560 |
| Appearance of Characters | Lyophilized solid |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| InChIKey | SHCXABJSXUACKU-WUTQZGRKSA-N |
| SMILES | COC(CC=CC=CCCC=CCC(C)C=CC(=CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O)C(C)=CC=C(C)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 100 mg/ml) or in Water (up to 1 mg/ml). |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;half-mask respirator (US);multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Changes in mitochondrial membrane potential during staurosporine-induced apoptosis in Jurkat cells.
FEBS Lett. 475 , 267, (2000) Cytochrome c release from mitochondria is central to apoptosis, but the events leading up to it are disputed. The mitochondrial membrane potential has been reported to decrease, increase or remain unc... |
|
|
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis.
Genes Dev. 13 , 1899, (1999)
|
|
|
Hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis is CD95-independent, requires the release of mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species and the activation of NF-kappaB.
Oncogene 18 , 747, (1999) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in cell death induced by many different stimuli. This study shows that hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in T-cells did not require tyrosine kina... |
| Bongkrekic Acid, Triammonium Salt |
| BONGKREKIC ACID |
| Bongkrekic acid solution |