Acerogenin G
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 10:17:54
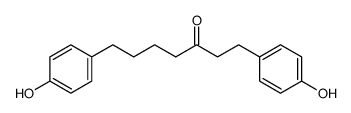
Acerogenin G structure
|
Common Name | Acerogenin G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 130233-83-9 | Molecular Weight | 298.38 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Acerogenin GAcerogenin G is a synthetic diarylheptane. Acerogenin G is first isolated from Acer nikoense[1]. |
| Name | 3-platyphyllone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Acerogenin G is a synthetic diarylheptane. Acerogenin G is first isolated from Acer nikoense[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C19H22O3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 298.38 |
| Exact Mass | 298.15700 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 4.01250 |
| Hazard Codes | N |
|---|
| 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptan-3-one |
| 1,7-bis(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanone |
| 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanone |
| acerogenin 3 |
| 1,7-Bis-(4-hydroxy-phenyl)-heptan-3-one |
| acerogenin G |
| 3-Platyphyllone |