Neticonazole hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 11:24:09
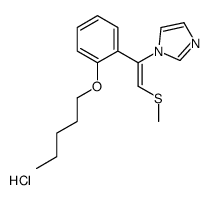
Neticonazole hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Neticonazole hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 130773-02-3 | Molecular Weight | 338.89500 | |
| Density | 1.06g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 464ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H23ClN2OS | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 234.4ºC | |
Use of Neticonazole hydrochlorideNeticonazole hydrochloride is an imidazole derivative and a potent and long-acting antifungal agent. Neticonazole hydrochloride is also an orally active exosome biogenesis and secretion inhibitor. Neticonazole hydrochloride has anti-infection and anti-cancer effects[1][2][3]. |
| Name | 1-[(E)-2-methylsulfanyl-1-(2-pentoxyphenyl)ethenyl]imidazole,hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Neticonazole hydrochloride is an imidazole derivative and a potent and long-acting antifungal agent. Neticonazole hydrochloride is also an orally active exosome biogenesis and secretion inhibitor. Neticonazole hydrochloride has anti-infection and anti-cancer effects[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Fungal [1] Exosome secretion[2] |
| In Vitro | Neticonazole (10 µM; 48 hours; C4-2B cells) treatment decreases the levels of both Alix and Rab27a, and significantly decreases nSMase2 levels. Neticonazole causes a significant inhibition in p-ERK levels[2]. Neticonazole (0-10 µM) exhibits a potent and dose-dependent inhibition of exosome release from C4-2B cells[2].Imidazole, antifungal, long-acting, exosome, secretion, anti-cancer, colorectal, p-ERK, anti-infection, nSMase2 Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: C4-2B cells Concentration: 10 µM Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Decreased the levels of both Alix and Rab27a, and significantly decreased nSMase2 levels. |
| In Vivo | Neticonazole (1-100 ng/kg; oral gavage; daily; for 15 days; male C57BL/6 mice) treatment significantly improves the survival of intestinal dysbacteriosis (IDB) mice with colorectal cancer (CRC) xenograft tumors, likely through increasing apoptosis of CRC xenograft tumor cells[3]. Animal Model: Male C57BL/6 mice (8 weeks old) given ampicillin, neomycin, metronidazole and vancomycin, and injected with SW480 cells[3] Dosage: 1 ng/kg, 10 ng/kg and 100 ng/kg Administration: Oral gavage; daily; for 15 days Result: Significantly improved the survival of IDB mice with CRC xenograft tumors. |
| References |
| Density | 1.06g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 464ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H23ClN2OS |
| Molecular Weight | 338.89500 |
| Flash Point | 234.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 338.12200 |
| PSA | 52.35000 |
| LogP | 5.46380 |
| Vapour Pressure | 8.66E-09mmHg at 25°C |
| InChIKey | HAHMABKERDVYCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCOc1ccccc1C(=CSC)n1ccnc1.Cl |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Atolant |
| SS717 |
| Newral |
| Neticonazole HCl |
| neticonazole |
| neticonazole hydrochloride |