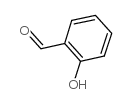
2-HBA

2-HBA structure
|
Common Name | 2-HBA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 131359-24-5 | Molecular Weight | 266.291 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 495.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H14O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 267.6±23.8 °C | |
Use of 2-HBA2-HBA is a potent inducer of NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) which can also activate caspase-3 and caspase-10. |
| Name | 2-hba |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 2-HBA is a potent inducer of NAD(P)H:quinone acceptor oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) which can also activate caspase-3 and caspase-10. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Caspase-3 Caspase-10 |
| In Vitro | When L1210 cells are exposed to 0.6 μM 2-HBA (bis(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)acetone), the specific activities of NQO1 and glutathione reductase increase by 6- and 1.5-fold, respectively. The total cellular glutathione content is also coordinately induced by 2.4-fold. In a more detailed study it is found that NQO1 is induced by 2-HBA in a concentration-dependent manner. Treatments with 2-HBA cause cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in both L1210 wild type cells and their Y8 drug-resistant counterparts in a concentration-dependent manner. 2-HBA can also activate caspase-3 and caspase-10[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Cells (20,000 per well) are grown for 24 h in 96-well plates, then exposed to 2-HBA (bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene)acetone) for either 24 h (for glutathione determination) or 48 h (for determination of enzyme activities). At the end of the exposure period, cells are collected by centrifugation (1500×g for 15 min at 4°C), washed with DPBS, and finally lysed in 0.08% digitonin. An aliquot (25 μL) is used for protein analysis. Activity of NQO1 is determined by the Prochaska test[1]. |
| Cell Assay | After exposure to 2-HBA (bis(2-hydroxybenzylidene)acetone) for 24 h, duplicate aliquots of cells (1×106) are collected by centrifugation and washed with cold DPBS. Apoptosis is determined using the Annexin-V-FLUOS assay with simultaneous determination of the necrotic fraction by the uptake of propidium iodide[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 495.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H14O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 266.291 |
| Flash Point | 267.6±23.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 266.094299 |
| PSA | 57.53000 |
| LogP | 4.91 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.704 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~80% 
2-HBA CAS#:131359-24-5 |
| Literature: Goswami, Shyamaprosad; Chakrabarty, Rinku Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 2011 , vol. 88, # 4 p. 547 - 557 |
|
~% 
2-HBA CAS#:131359-24-5 |
| Literature: Heilbron; Buck Journal of the Chemical Society, 1921 , vol. 119, p. 1514 |
|
~% 
2-HBA CAS#:131359-24-5 |
| Literature: McGookin; Sinclair Journal of the Chemical Society, 1928 , p. 1175 |
|
~% 
2-HBA CAS#:131359-24-5 |
| Literature: Glaser; Tramer Journal fuer Praktische Chemie (Leipzig), 1927 , vol. <2>116, p. 334,336 |
|
~% 
2-HBA CAS#:131359-24-5 |
| Literature: McGookin; Heilbron Journal of the Chemical Society, 2102, 2103 |
|
Functional Analysis of Chicken IRF7 in Response to dsRNA Analog Poly(I:C) by Integrating Overexpression and Knockdown.
PLoS ONE 10 , e0133450, (2015) In order to develop novel strategies to protect against increasingly virulent bird-linked pathogens, a better understanding of the avian antiviral response mechanism is essential. Type I interferons (... |
| 1,4-Pentadien-3-one, 1,5-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-, (1E,4E)- |
| (1E,4E)-1,5-Bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)penta-1,4-dien-3-one |
| QR B1U1V1U1R BQ &&(E,E)- Form |
| (1E,4E)-1,5-Bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one |

![2,2'-spirobi[chromene] structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/214/178-30-3.png)
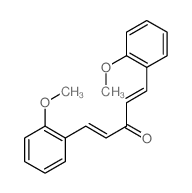 CAS#:41973-42-6
CAS#:41973-42-6