sodium ascorbate
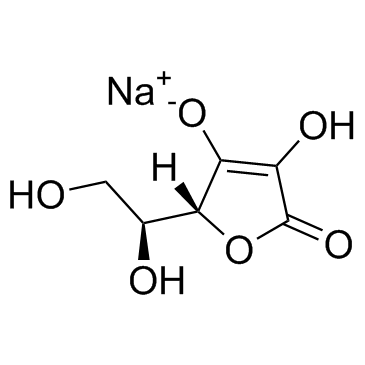
sodium ascorbate structure
|
Common Name | sodium ascorbate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 134-03-2 | Molecular Weight | 198.106 | |
| Density | 1.799 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 552.7ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H7NaO6 | Melting Point | 220 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 238.2ºC | |
Use of sodium ascorbateL-Ascorbic acid (sodium) is a more bioavailable form of vitamin C that is an antioxidant agent. |
| Name | Sodium L-Ascorbate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Ascorbic acid (sodium) is a more bioavailable form of vitamin C that is an antioxidant agent. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid), a known enhancer of collagen deposition, has also been identified as an inhibitor of elastogenesis[1]. The conditioned medium for B16F10 cells significantly inhibits cell apoptosis induced by sodium L-ascorbate (10 mM), and the effective ingredients in the medium show a relative molecular mass below 5,000[2]. |
| In Vivo | Tg rats treated with sodium L-ascorbate show a higher incidence of carcinoma (29.6%), compared to those without sodium L-ascorbate (15.4%). Independent of the sodium L-ascorbate treatment, transgenic rats exhibit various kinds of malignant tumors in various organs[3]. After 12 weeks of PEITC-treatment, both simple hyperplasia and papillary or nodular (PN) hyperplasia have developed in all animals, but the majority of these lesions have disappeared at week 48, irrespective of the sodium L-ascorbate-treatment. The same lesions after 24 weeks of PEITC-treatment have progressed to dysplasia and carcinoma, in a small number of cases by week 48, but enhancement by the sodium L-ascorbate-treatment is evident only with simple hyperplasias and PN hyperplasias in rats[4]. |
| Animal Admin | A total of 40 7-week-old male Tg rats are divided into 2 groups. Twenty-seven (group 1) and 13 (group 2) rats are given a powdered MF diet with or without 5% sodium L-ascorbate, respectively. Similarly, a total of 42 7-week-old male Non-tg rats are divided into 2 groups, and 30 (group 3) and 12 (group 4) animals are given a diet with or without 5% sodium L-ascorbate, respectively. |
| References |
| Density | 1.799 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 552.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 220 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H7NaO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 198.106 |
| Flash Point | 238.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 198.014038 |
| PSA | 110.05000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.62E-14mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 105.5 ° (C=10, H2O) |
| Water Solubility | 620 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
|
Overexpression of heme oxygenase 1 causes cognitive decline and affects pathways for tauopathy in mice.
J. Alzheimers Dis. 43(2) , 519-34, (2014) The stress protein heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) is upregulated and co-localizes to pathological features, including tauopathies in the brains of individuals with Alzheimer's disease. However, the relations... |
|
|
Redox-based probes as tools to monitor oxidized protein tyrosine phosphatases in living cells.
Eur. J. Med. Chem. 88 , 28-33, (2014) Reversible oxidation of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) has emerged as an important regulatory mechanism whereby reactive oxygen species (ROS) inactivates the PTP and promotes phosphorylation and... |
|
|
Design, Preparation, and Characterization of Zn and Cu Metallopeptides Based On Tetradentate Aminopyridine Ligands Showing Enhanced DNA Cleavage Activity.
Inorg. Chem. 54 , 10542-58, (2015) The conjugation of redox-active complexes that can function as chemical nucleases to cationic tetrapeptides is pursued in this work in order to explore the expected synergistic effect between these tw... |
| EINECS 205-126-1 |
| Sodium ascorbate |
| L-Ascorbic Acid Sodium Salt |
| Vitamine C sodium salt,Vitamin C sodium salt |
| (+)-Sodium L-ascorbate (L(+)-Ascorbic acid sodium salt |
| SodiuM L-Ascorbate |
| L(+)-Ascorbic acid sodium salt,Vitamin C sodium salt |
| MFCD00082340 |
| Vitamin C Sodium Salt |
| L(+)-Ascorbic acid sodium salt,E301 |
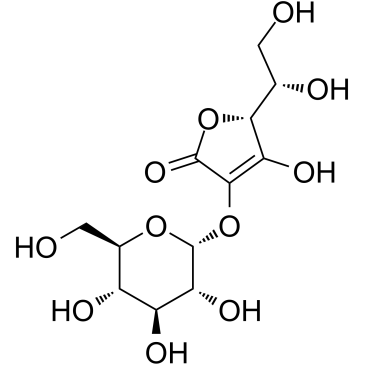 CAS#:129499-78-1
CAS#:129499-78-1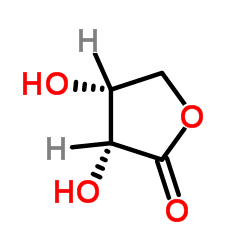 CAS#:15667-21-7
CAS#:15667-21-7
