Thailanstatin A
Modify Date: 2024-01-03 18:26:55
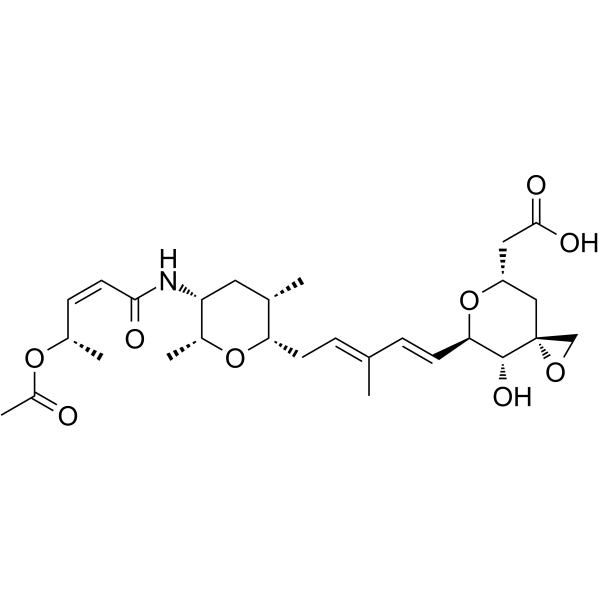
Thailanstatin A structure
|
Common Name | Thailanstatin A | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1426953-21-0 | Molecular Weight | 535.63 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H41NO9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Thailanstatin AThailanstatin A is an ultra-potent inhibitor of eukaryotic RNA splicing (IC50=650 nM). Thailanstatin A exerts effects via non-covalent binding to the SF3b subunit of the U2 snRNA subcomplex of the spliceosome and shows low-nM to sub-nM IC50s against multiple cancer cell lines. Thailanstatin A, a payload for ADCs, is conjugated to the lysines on trastuzumab yielding “linker-less” ADC[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Thailanstatin A |
|---|
| Description | Thailanstatin A is an ultra-potent inhibitor of eukaryotic RNA splicing (IC50=650 nM). Thailanstatin A exerts effects via non-covalent binding to the SF3b subunit of the U2 snRNA subcomplex of the spliceosome and shows low-nM to sub-nM IC50s against multiple cancer cell lines. Thailanstatin A, a payload for ADCs, is conjugated to the lysines on trastuzumab yielding “linker-less” ADC[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Thailanstatin A (TST-A) is a potent antiproliferative natural product discovered by our group from Burkholderia thailandensis MSMB43[2]. Thailanstatin A (DU-145, NCI-H232A, MDA-MB-231 and SKOV-3 cells) exhibits potent antiproliferative activities with GI50s in the single nM range (1.11-2.69 nM)[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C28H41NO9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 535.63 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |