Quinaprilat
Modify Date: 2025-10-22 19:56:08
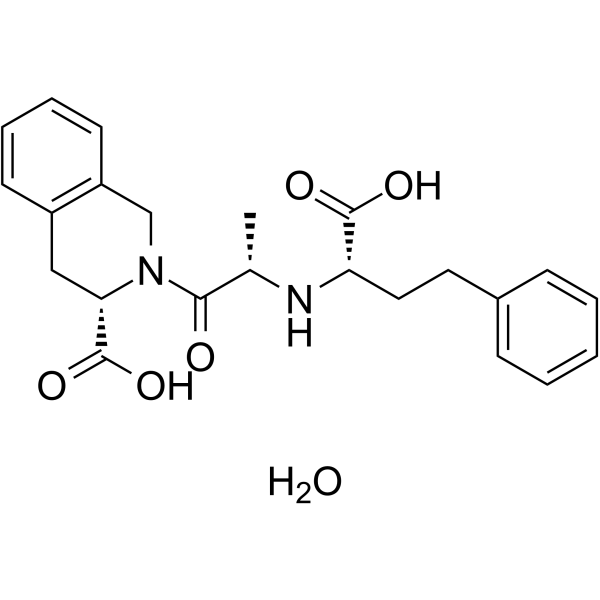
Quinaprilat structure
|
Common Name | Quinaprilat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1435786-09-6 | Molecular Weight | 456.53100 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C25H32N2O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of QuinaprilatQuinaprilat hydrate is a non-mercapto Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, the active metabolite of Quinapril. Quinaprilat hydrate specifically blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibits the degradation of bradykinin. Quinaprilat hydrate acts as anti-hypertensive agent and vasodilator[1][2]. |
| Name | (3S)-2-[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]propanoyl]-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid,hydrate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Quinaprilat hydrate is a non-mercapto Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, the active metabolite of Quinapril. Quinaprilat hydrate specifically blocks the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II and inhibits the degradation of bradykinin. Quinaprilat hydrate acts as anti-hypertensive agent and vasodilator[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Quinaprilat hydrate (5 μM) mediates the interaction of organic anion transporter 3 (hOAT3) which can promote renal active secretion of quinapril that increases uptake of quinaprilat to 25-fold in HEK293 cells and hOAT3 affinity Km for quinaprilat is 13.4 μM[1]. Quinaprilat hydrate (100 nM, 20 min) can inhibit the activity of protein kinase C (PKC) by activing the B1 receptor resulting in the release of NO in human lung microvascular endothelial (HLMVE) cells[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C25H32N2O6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 456.53100 |
| Exact Mass | 456.22600 |
| PSA | 105.17000 |
| LogP | 2.83160 |
| InChIKey | OFYSYEOWQQCPEU-ZAFWUOJLSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(NC(CCc1ccccc1)C(=O)O)C(=O)N1Cc2ccccc2CC1C(=O)O.O |
| Quinapril diacid [MI] |
| 3-Isoquinolinecarboxylic acid,2-(2-((1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)amino)-1-oxopropyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-,(3S-(2(R*(R*)),3R*))-,monohydrate |
| Quinapril diacid |
| Quinaprilat hydrate [WHO-DD] |