Mastoparan 7 trifluoroacetate salt
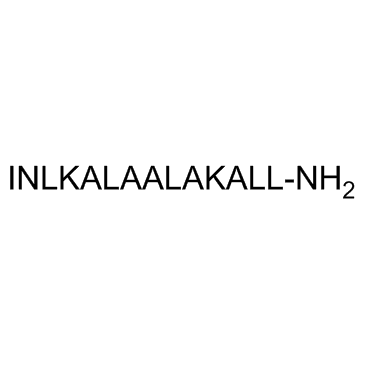
Mastoparan 7 trifluoroacetate salt structure
|
Common Name | Mastoparan 7 trifluoroacetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 145854-59-7 | Molecular Weight | 1421.81 | |
| Density | 1.154g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1649.9ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C67H124N18O15 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 951.6ºC | |
Use of Mastoparan 7 trifluoroacetate saltMas7, a structural analogue of mastoparan, is an activator of heterotrimeric Gi proteins and its downstream effectors. |
| Name | Mastoparan-7 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Mas7, a structural analogue of mastoparan, is an activator of heterotrimeric Gi proteins and its downstream effectors. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Mas7 produces several biological effects in different cell types. The effect of Mas7 on endogenous mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity is in the micromolar range with a maximal activation of 205% over the basal. In pertussis treated plasma membranes, it is found that the effect of Mas7 on endogenous mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase is partially blocked, which suggests the involvement of G-proteins, such as Gi or G0[1]. Mas7 is a basic tetradecapeptide isolated from isp venom, which activates guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G-proteins) and stimulates apoptosis. In smooth muscle cells, Mas7 leads to an increase in the perfusion pressure. Vascular contraction is induced by Mas7. The vasoconstriction triggered by mas-7 exhibited a slower increase compared to that simulated by phenylephrine or vasopressin[2]. Exposure of hippocampal neurons to a low dose of Mas-7 increases dendritic spine density and spine head width in a time-dependent manner. Additionally, Mas-7 enhances postsynaptic density protein-95 (PSD-95) clustering in neurites and activates Gαo signaling, increasing the intracellular Ca2+ concentration[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Hippocampal neurons cultured in round 35 mm coverslips at a density of 160,000 cells/coverslip are transfected with EGFP at 11 DIV. Then, at 14 DIV the neurons are placed in the imaging chamber in an isotonic solution. The EGFP-positive neurons are imaged with microscope every 5 min for 45 min after the treatment with 1 μM Mas-7. The images are processed and analyzed using ImageJ software[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.154g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1649.9ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C67H124N18O15 |
| Molecular Weight | 1421.81 |
| Flash Point | 951.6ºC |
| PSA | 644.54000 |
| LogP | 5.49270 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.523 |
| InChIKey | HOLQXBRPSSZJMZ-FGRXCANLSA-N |
| SMILES | CCC(C)C(N)C(=O)NC(CC(N)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(N)=O |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Activation of GTP formation and high-affinity GTP hydrolysis by mastoparan in various cell membranes. G-protein activation via nucleoside diphosphate kinase, a possible general mechanism of mastoparan action.
Biochem. Pharmacol. 51 , 217-223, (1996) The wasp venom, mastoparan (MP), is a direct activator of reconstituted pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins and of purified nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) [E.C. 2.6.4.6.]. In HL-60 membranes, M... |
|
|
The heterotrimeric G-protein Gi is localized to the insulin secretory granules of beta-cells and is involved in insulin exocytosis.
J. Biol. Chem. 270 , 12869, (1995) Mastoparan, a tetradecapeptide found in wasp venom that stimulates G-proteins, increases insulin secretion from beta-cells. In this study, we have examined the role of heterotrimeric G-proteins in mas... |
|
|
Mastoparan may activate GTP hydrolysis by Gi-proteins in HL-60 membranes indirectly through interaction with nucleoside diphosphate kinase.
Biochemistry 304 , 377-383, (1994) The wasp venom, mastoparan (MP), activates reconstituted pertussis toxin (PTX)-sensitive G-proteins in a receptor-independent manner. We studied the effects of MP and its analogue, mastoparan 7 (MP 7)... |
| Mastoparan from Polistes jadwagae |
| MAS 7 |
| Mas7 |

