β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride
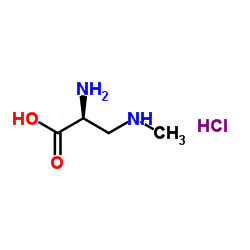
β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16012-55-8 | Molecular Weight | 154.595 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H11ClN2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochlorideβ-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride (BMAA hydrochloride) is a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria, could cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and possibly other neurodegenerative diseases[1][2][3]. |
| Name | S(+)-2-Amino-3-(methylamino)propionic acid hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | β-N-methylamino-L-alanine hydrochloride (BMAA hydrochloride) is a neurotoxin produced by cyanobacteria, could cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and possibly other neurodegenerative diseases[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[2]. Cox PA, et, al. BMAA and Neurodegenerative Illness. Neurotox Res. 2018 Jan; 33(1): 178-183. |
| Molecular Formula | C4H11ClN2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 154.595 |
| Exact Mass | 154.050903 |
| PSA | 75.35000 |
| LogP | 0.51090 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H332-H315-H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P301 + P312 + P330-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
| HS Code | 2922499990 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2922499990 other amino-acids, other than those containing more than one kind of oxygen function, and their esters; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:AB(certificate of inspection for goods inward,certificate of inspection for goods outward) MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Improving derivatization efficiency of BMAA utilizing AccQ-Tag in a complex cyanobacterial matrix.
Amino Acids 36 , 43-8, (2009) Two different assays have been developed and used in order to investigate the optimal conditions for derivatization and detection of acid beta-N-methyl-amino-L-alanine (BMAA) in a cyanobacterial sampl... |
|
|
Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia linked to a plant excitant neurotoxin.
Science 237 , 517, (1987) The decline in the high incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, parkinsonism, and Alzheimer-type dementia among the Chamorro population of the western Pacific islands of Guam and Rota, coupled wit... |
|
|
Beta-N-methylamino-L-alanine (L-BMAA) is a potent agonist of 'metabolotropic' glutamate receptors.
Eur. J. Pharmacol. 181 , 327-328, (1990)
|
| L-BMAA hydrochloride |
| (S)-2-Amino-3-(methylamino)propanoic acid hydrochloride |
| L-Alanine, 3-(methylamino)-, hydrochloride (1:1) |
| 3-(Methylamino)-L-alanine hydrochloride (1:1) |
| (2S)-2-amino-3-(methylamino)propanoic acid,hydrochloride |

