| Description |
WAY-100635 is a potent and selective 5-HT1A Receptor antagonist with a pIC50 of 8.87, an apparent pA2 of 9.71.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
5-HT1A Receptor:8.87 (pIC50)
5-HT1A Receptor:9.71 (pA2)
|
| In Vitro |
WAY-100635 is a potent and, at high concentrations, an insurmountable antagonist of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist action of 5-carboxamidotryptamine, with an apparent pA2 value (at 0.3 nM) of 9.71. WAY-100635 displaces specific binding of the 5-HT1A radioligand, [3H]8-OH-DPAT (8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin), to rat hippocampal membranes with a plCIC50 of 8.87[1].
|
| In Vivo |
Administration of (S)-WAY-100135 (0.025-1.0 mg/kg i.v.) moderately depresses neuronal activity at all doses tested. In contrast, administration of WAY-100635 (0.025-0.5 mg/kg i.v.) significantly increases neuronal activity. The stimulatory action of WAY-100635, like that of spiperone, is evident during wakefulness but not during sleep. Pretreatment with (S)-WAY-100135 (0.5 mg/kg i.v.) weakly attenuates the inhibitory action of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin. In contrast, WAY-100635 at doses as low as 0.1 mg/kg i.v. completely blockes the action of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin. The antagonist action of WAY-100635 at 5-HT1A autoreceptors closely parallels its ability to increase neuronal activity. Overall, WAY-100635 appears to act as a selective 5-HT1A antagonist, whereas (S)-WAY-100135 does not. The results obtained with WAY-100635 confirm our previous findings obtained with spiperone and further support the hypothesis that 5-HT1A autoreceptor-mediated feedback inhibition operates under physiological conditions[2].
|
| References |
[1]. Forster EA, et al. A pharmacological profile of the selective silent 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY-100635. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Jul 25;281(1):81-8. [2]. Fornal CA, et al. WAY-100635, a potent and selective 5-hydroxytryptamine1A antagonist, increases serotonergic neuronal activity in behaving cats: comparison with (S)-WAY-100135. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Aug;278(2):752-62.
|
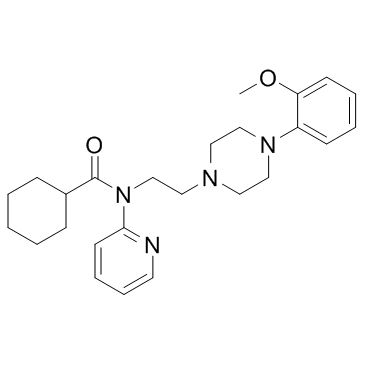
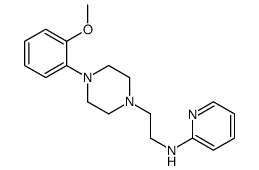 CAS#:155204-28-7
CAS#:155204-28-7 CAS#:2719-27-9
CAS#:2719-27-9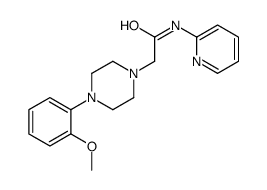 CAS#:146714-63-8
CAS#:146714-63-8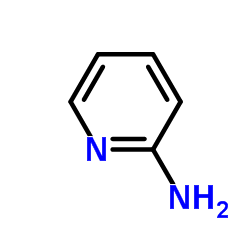 CAS#:504-29-0
CAS#:504-29-0 CAS#:5221-37-4
CAS#:5221-37-4 CAS#:98-89-5
CAS#:98-89-5 CAS#:35386-24-4
CAS#:35386-24-4