Lificiguat

Lificiguat structure
|
Common Name | Lificiguat | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 170632-47-0 | Molecular Weight | 304.342 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 522.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C19H16N2O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 269.6±30.1 °C | |
Use of LificiguatLificiguat binds to the β subunit of soluble guanylyl cyclase(sGC) with Kd of 0.6-1.1 μM in the presence of CO. |
| Name | yc-1 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Lificiguat binds to the β subunit of soluble guanylyl cyclase(sGC) with Kd of 0.6-1.1 μM in the presence of CO. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 0.6-1.1 μM (sGC, in the presence of CO)[1] |
| In Vitro | Soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) is a heterodimeric heme protein and the primary NO receptor. Lificiguat (YC-1) binds near or directly to the heme-containing domain of the beta subunit. In the absence of CO, Lificiguat (YC-1) binds with Kd=9-21 μM, depending on construct. In the presence of CO, these values decrease to 0.6-1.1 μM. Lificiguat (YC-1) greatly enhanced CO binding to heterodimeric sGC, as expected (Kd=1 μM). Lificiguat (YC-1) stimulates sGC two- to four-fold in the absence of NO but acts synergistically with CO or NO to achieve several hundred fold activation. Binding of Lificiguat(YC-1) can also overcome inhibitory phosphorylation of sGC[1]. Lificiguat (YC-1) is a soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) activator. HCC cell lines HepG2, BEL-7402 and HCCLM3 are incubated for 72 h with Sorafenib and/or Lificiguat (YC-1). Sorafenib or Lificiguat (YC-1) alone inhibits HCC cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, combination of Sorafenib and Lificiguat (YC-1) significantly suppresses proliferation of HCC cells in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, at the ED50 doses for both Sorafenib and Lificiguat (YC-1), combination index values (CI)=0.93 in HepG2, 0.95 in BEL-7402 and 0.72 in HCCLM3 respectively, suggesting that Sorafenib and Lificiguat (YC-1) synergistically inhibit proliferation of HCC cells[2]. |
| In Vivo | Lificiguat (YC-1) (30 or 60 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits MDA-MB-468 tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner. The effect of the prodrug formulation of Lificiguat (YC-1), YC-1-S, in MDA-MB-468 tumor-bearing mice is also investigated. In vivo pharmacokinetic analysis reveal that YC-1-S is quickly converted into its active form. Mice are administered 20, 40 or 80 mg/kg YC-1-S p.o. YC-1-S also displays dose-dependent inhibition of MDA-MB468 tumor growth. Both Lificiguat (YC-1) and YC-1-S dose-dependently reduce tumor weight. Moreover, the mean body weight of mice is not affected by Lificiguat (YC-1) or YC-1-S compare with vehicle-treated groups[3]. Lificiguat (YC-1) is a potent NO-GC activator reported to improve rodent learning behavior when examined with the Morris water maze (MWM) and avoidance tests. Lificiguat (YC-1) enhances long-term potentiation (LTP) in hippocampal Schafer collateral-CA1 synapse via the NO-cGMP-PKG-dependent pathway and potentiated LTP induction in the amygdala, increases the activation of ERK, and potentiated the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) in response to fear memory test[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | CO dissociation constants are measured by titrating CO from a saturated solution into sGC protein and monitoring the appearance of the CO-bound Soret absorption band. The Ms sGC β1(1-380) and Bt sGC β1(1-197) samples are prepared in Ar-purged buffer supplemented with excess dithionite. CO binding experiments are performed in a 10 cm pathlength cuvette for Ms sGC-β1(1-380) and Ms sGC-NT21 using a Cary 50 spectrophotometer with a modified sample holder. Binding data in the presence and absence of 50 μM Lificiguat (YC-1) is plotted using a single site saturation ligand binding model in SigmaPlot[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cell proliferation assay is measured using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, cells are cultured in 96-well plates at a concentration of 3×103/well, incubated for 24 h, and treated with Sorafenib and/or Lificiguat (YC-1). After 72 h treatment, CCK-8 reagent is added to each well. The absorbance is measured at 450 nm after 2.5 h incubation at 37°C using an automated ELISA plate reader. Any synergistic effects resulting from combination of the compounds are measured using Microsoft Excel software to determine the combination index values (CI>1: antagonistic effect, CI=1: additive effect, and CT<1: synergistic effect)[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[3] Fifty-eight female nu/nu mice (4 weeks-old) are used. MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells (5×106 cells per mouse) are suspended in 0.1 mL of Matrigel solution (50% v/v Matrigel in PBS) and inoculated into the mammary fat pads of nude mice. When the tumor masses reach 100 mm3, the tumor-bearing mice are randomly divided into groups for treatments with different Lificiguat (YC-1)/YC-1-S doses. The mice are i.p. injected with YC-1 (30 or 60 mg/kg) or administered YC-1-S p.o. Tumor size and mouse body weight are measured once every 3 days, and tumor volume (mm3) is calculated using the equation: length×(width)2×0.5. At the end of the experiments, mice are killed and tumor nodules are dissected and weighed. Tumor tissues are subjected to Western blotting. Rats[4] 4-month-old (200-250 g) and 24-month-old (550-600 g) male Wistar-albino rats are used. Lificiguat (YC-1) is prepared immediately prior to use and given intraperitoneally (i.p.) in a volume of 0.1 mL per 100 g body weight. All rats receives 1 mg/kg/day of Lificiguat (YC-1) for 2 weeks. DMSO is administered to 4-month-old and 24-month-old rats (n=10, for each group). Doses are selected to confirm the selected doses on locomotor activity; all results are measured. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 522.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C19H16N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 304.342 |
| Flash Point | 269.6±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 304.121185 |
| PSA | 51.19000 |
| LogP | 3.55 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.653 |
| InChIKey | OQQVFCKUDYMWGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | OCc1ccc(-c2nn(Cc3ccccc3)c3ccccc23)o1 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
VAV3 mediates resistance to breast cancer endocrine therapy.
Breast Cancer Res. 16(3) , R53, (2014) Endocrine therapies targeting cell proliferation and survival mediated by estrogen receptor α (ERα) are among the most effective systemic treatments for ERα-positive breast cancer. However, most tumor... |
|
|
Stimulation of the cardiac myocyte Na+-K+ pump due to reversal of its constitutive oxidative inhibition.
Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 309 , C239-50, (2015) Protein kinase C can activate NADPH oxidase and induce glutathionylation of the β1-Na(+)-K(+) pump subunit, inhibiting activity of the catalytic α-subunit. To examine if signaling of nitric oxide-indu... |
|
|
The cyclic GMP/protein kinase G pathway as a therapeutic target in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancer Lett. 370 , 279-85, (2015) Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is an aggressive disease with high mortality. Treatments, which can result in significant morbidity, have not substantially changed in three decades. The ... |
| 2-{1-[(2R)-2-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-2-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yloxy)ethyl]-5-methyl-6-(1,3-oxazol-2-yl)-2,4-dioxo-1,4-dihydrothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-3(2H)-yl}-2-methylpropanoic acid |
| Thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine-3(2H)-acetic acid, 1,4-dihydro-1-[(2R)-2-(2-methoxyphenyl)-2-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)oxy]ethyl]-α,α,5-trimethyl-6-(2-oxazolyl)-2,4-dioxo- |
| ND-630 |
| GS-0976 |
| NDI-010976 |
| (5-(1-benzyl-1H-indazol-3-yl)furan-2-yl)methanol |
| YC-1 |
 CAS#:170632-13-0
CAS#:170632-13-0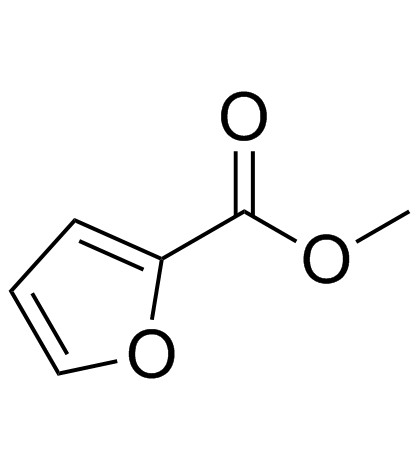 CAS#:611-13-2
CAS#:611-13-2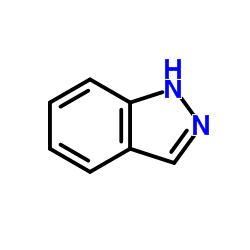 CAS#:271-44-3
CAS#:271-44-3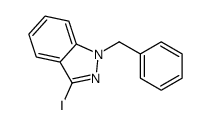 CAS#:205643-28-3
CAS#:205643-28-3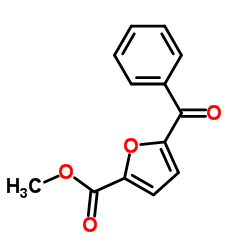 CAS#:58972-21-7
CAS#:58972-21-7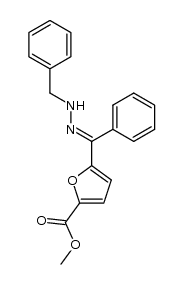 CAS#:170632-18-5
CAS#:170632-18-5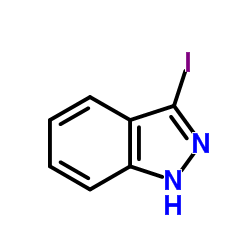 CAS#:66607-27-0
CAS#:66607-27-0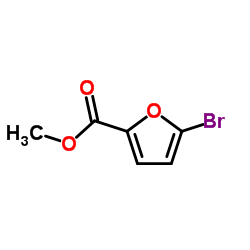 CAS#:2527-99-3
CAS#:2527-99-3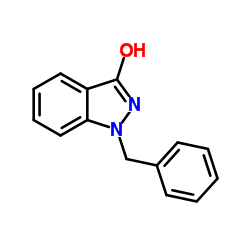 CAS#:2215-63-6
CAS#:2215-63-6