pp1
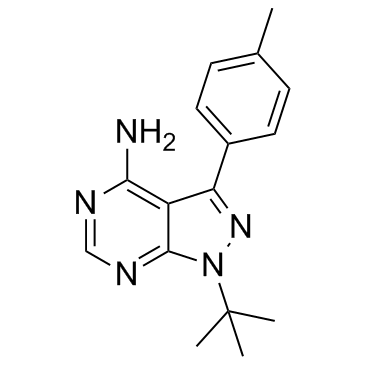
pp1 structure
|
Common Name | pp1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 172889-26-8 | Molecular Weight | 281.356 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 478.8±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19N5 | Melting Point | 205-207ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 243.4±27.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of pp1PP1 is a potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50 of 5 and 6 nM for Lck and Fyn, respectively. |
| Name | 4-Amino-1-tert-butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | PP1 is a potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor with IC50 of 5 and 6 nM for Lck and Fyn, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 5 nM (Lck), 6 nM (Fyn), 250 nM (EGFR), >50 μM (JAK2)[1] |
| In Vitro | PP1 inhibits Lck (IC50=5 nM) and FynT (IC50=6 nM) in vitro at concentrations significantly lower than those required to inhibit ZAP-70 (IC50>100 μM), JAK2 (IC50>50 μM), the EGFR kinase, and protein kinase A. PP1 inhibits whole cell tyrosine phosphorylation and proliferation in T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 and mitogens. PP1 selectively inhibits IL-2 gene expression over GM-CSF and IL-2R gene induction in human T cells[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Protein A-Sepharose beads (prepared as a 50% (w/v) suspension) are added to the antibody/lysate mixture at 250 μL/mL and allowed to incubate for 30 min at 4°C. The beads are then washed twice in 1 mL of lysis buffer and twice in 1 mL of kinase buffer (25 mM HEPES, 3 mM MnCl2, 5 mM MgCl2, and 100 μM sodium orthovanadate) and resuspended to 50% (w/v) in kinase buffer. Twenty-five microliters of the bead suspension is added to each well of the enolase-coated 96-well high protein binding plate together with an appropriate concentration of compound and [γ-32P]ATP (25 μL/well of a 200 μCi/mL solution in kinase buffer). After incubation for 20 min at 20°C, 60 μL of boiling 2× solubilization buffer containing 10 mM ATP is added to the assay wells to terminate the reactions. Thirty microliters of the samples is removed from the wells, boiled for 5 min, and run on a 7.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The gels are subsequently dried and exposed to Kodak X-AR film. For quantitation, films are scanned using a Molecular Dynamics laser scanner, and the optical density of the major substrate band, enolase p46, is determined. Concentrations of compound that causes 50% inhibition of enolase phosphorylation (IC50) are determined from a plot of the density versus concentration of compound. In companion experiments for measuring the activity of compounds against Lck, the assay plate is washed with two wash cycles on a Skatron harvester using 50 mM EDTA, 1 mM ATP. Scintillation fluid (100 μL) is then added to the wells, and P incorporation is measured using a Pharmacia Biotech micro-β-counter. Concentrations of compound that causes 50% inhibition of enzyme activity (IC50) are determined from a plot of the percent inhibition of enzyme activity versus concentration of compound[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Inhibition of anti-CD3-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation in purified human peripheral blood T cells is measured as follows. All incubations are carried out at 37°C in an Eppendorf Thermomixer 5436 at a mixing setting of 11. Cells (1×106 in 100 μL of RPMI 1640 medium) are incubated for 15 min with drug prior to a 6-min incubation with 1 μg of anti-CD3/mL (anti-leu4, 100 μg/mL). The final volume of the reaction is 115 μL. Reactions are terminated by the addition of 57.5 μL of 3× solubilization buffer incubated at 100°C prior to its addition. Samples are mixed, boiled for 5 min, and stored at -70°C. Western blots of these cell lysates, run on 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gels, are probed with a polyclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antibody, and immune complexes are detected with I-labeled protein A (ICN). For quantitation, films are scanned using a Molecular Dynamics laser scanner, and the optical densities of the major substrate band, p70, are quantitated in the presence of anti-CD3 (in the presence and absence of drug). Percent inhibition is calculated as follows: (1-(p70 optical density units in presence of drug/p70 units in absence of drug))×100. IC50 equals the concentration of compound at which 50% inhibition is measured[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 478.8±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 205-207ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C16H19N5 |
| Molecular Weight | 281.356 |
| Flash Point | 243.4±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 281.164032 |
| PSA | 69.62000 |
| LogP | 3.11 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.652 |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at +4°C |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: >20mg/mL |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Phrases | 22 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Control of the pericentrosomal H2O2 level by peroxiredoxin I is critical for mitotic progression.
J. Cell Biol. 210 , 23-33, (2015) Proteins associated with the centrosome play key roles in mitotic progression in mammalian cells. The activity of Cdk1-opposing phosphatases at the centrosome must be inhibited during early mitosis to... |
|
|
p21-activated Kinases (PAKs) Mediate the Phosphorylation of PREX2 Protein to Initiate Feedback Inhibition of Rac1 GTPase.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 28915-31, (2015) Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3)-dependent Rac exchanger 2 (PREX2) is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) GTPase, facili... |
|
|
Calpain-mediated cleavage of DARPP-32 in Alzheimer's disease.
Aging Cell 14 , 878-86, (2015) Toxicity induced by aberrant protein aggregates in Alzheimer's disease (AD) causes synaptic disconnection and concomitant progressive neurodegeneration that eventually impair cognitive function. cAMP-... |
| 1-(tert-Butyl)-3-(p-tolyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine |
| 3-(4-Methylphenyl)-1-(2-methyl-2-propanyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine |
| 1-tert-butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine |
| 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine, 1-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl)- |
| 4-Amino-5-(methylphenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo-(3,4-d)pyrimidine |
| 1H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (1-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-3-(4-methylphenyl) |
| 1-tert-butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)-1h-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine |
| pp1 |