Riluzole
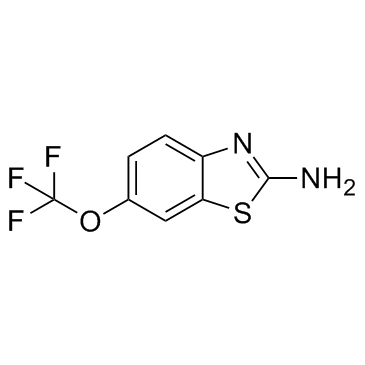
Riluzole structure
|
Common Name | Riluzole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1744-22-5 | Molecular Weight | 234.198 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 296.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H5F3N2OS | Melting Point | 116-118ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 133.0±30.1 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of RiluzoleRiluzole is an anticonvulsant drug and belongs to the family of use-dependent Na+ channel blocker which can also inhibit GABA uptake with an IC50 of 43 μM. |
| Name | 2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)benzo[d]thiazole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Riluzole is an anticonvulsant drug and belongs to the family of use-dependent Na+ channel blocker which can also inhibit GABA uptake with an IC50 of 43 μM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Sodium channel[1] IC50: 43 μM (GABA receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | Riluzole is an anticonvulsant drug and belongs to the family of use-dependent Na+ channel blocker which can also inhibit GABA uptake with an IC50 of 43 μM. At 20 μM, Riluzole inhibits peak autaptic IPSCs only slightly but prolongs IPSCs reliably. It is also found that Riluzole causes a strong, concentration-dependent, readily reversible enhancement of responses to 2 μM GABA. At higher concentrations of Riluzole, especially 300 μM, GABA currents exhibit apparent desensitization during prolonged co-exposure to 2 μM GABA and Riluzole. The EC50 of Riluzole potentiation of GABA responses is about 60 μM[1]. |
| In Vivo | In normal naïve rats, systemic injection of Riluzole (8 mg/kg, i.p.; n=6 rats) decreases the duration of ultrasonic but not audible vocalizations evoked by noxious stimulation of the knee joint compare to vehicle tested in the same rats (P<0.05). Systemic application of Riluzole (8 mg/kg, i.p.; n=19 rats) decreases the vocalizations of arthritic rats compare to predrug and vehicle significantly (P<0.05 to 0.001). Riluzole administered into the CeA significantly decreases the duration of audible and ultrasonic vocalizations evoked by noxious stimulation of the knee compare to predrug values (n=8 rats; P<0.05 to 0.01)[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Two-electrode voltage clamp of Xenopus oocytes expressing exogenous GABAA receptors is performed with a CA-1B high performance oocyte clamp. The extracellular recording solution is ND-96 medium. Riluzole is applied from a common tip via a gravity-driven multibarrel drug-delivery system. Data acquisition and analysis are performed with pCLAMP 6 software[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (180 to 350 g) are housed in a temperature-controlled room and maintained on a 12-h day/night cycle with unrestricted access to food and water. Pain behaviors are measured before and 5 h after induction of a mono-arthritis in the left knee joint. To test the effects of systemic (intraperitoneal, i.p.) application of Riluzole, pain behaviors are measured 1 h postinjection of Riluzole in normal and arthritic animals. To determine effects of Riluzole into the amygdala, pain behaviors are measured 15 min after starting Riluzole application through a stereotaxically implanted microdialysis probe. To investigate site of action in the amygdala of systemically applied Riluzole, potassium channel blockers are administered into the amygdala 45 min after systemic application of Riluzole and pain behaviors are measured 15 min later, i.e., 1 h postinjection of riluzole (i.p.)[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 296.3±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 116-118ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C8H5F3N2OS |
| Molecular Weight | 234.198 |
| Flash Point | 133.0±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 234.007462 |
| PSA | 76.38000 |
| LogP | 2.84 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.615 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
| Water Solubility | DMSO: ≥25 mg/mL |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H301 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P310 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type P2 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T:Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | R25 |
| Safety Phrases | S45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DL2830000 |
| Packaging Group | II |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|
~78% 
Riluzole CAS#:1744-22-5 |
| Literature: Anzini, Maurizio; Chelini, Alessia; Mancini, Alessandra; Cappelli, Andrea; Frosini, Maria; Ricci, Lorenzo; Valoti, Massimo; Magistretti, Jacopo; Castelli, Loretta; Giordani, Antonio; Makovec, Francesco; Vomero, Salvatore Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2010 , vol. 53, # 2 p. 734 - 744 |
|
~87% 
Riluzole CAS#:1744-22-5 |
| Literature: BRISTOL-MYERS SQUIBB COMPANY; UNIVERSITE DE MONTREAL; LAWRENCE, Michael, R.; MILLER, Michael, M.; SEIFFERT, Dietmar, Alfred; POSY, Shoshana, L.; WONG, Pancras, C.; BANVILLE, Jacques; RUEDIGER, Edward, H.; DEON, Daniel, H.; MARTEL, Alain; TREMBLAY, Francois; GUY, Julia; LAVALLEE, Jean-Francois; GAGNON, Marc Patent: WO2013/163244 A1, 2013 ; Location in patent: Paragraph 00205; 00206 ; |
|
~73% 
Riluzole CAS#:1744-22-5 |
| Literature: Jordan, Alfonzo D.; Luo, Chi; Reitz, Allen B. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2003 , vol. 68, # 22 p. 8693 - 8696 |
|
~% 
Riluzole CAS#:1744-22-5 |
| Literature: US5236940 A1, ; |
|
~% 
Riluzole CAS#:1744-22-5 |
| Literature: US5068238 A1, ; |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Cheminformatics analysis of assertions mined from literature that describe drug-induced liver injury in different species.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 171-83, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is one of the main causes of drug attrition. The ability to predict the liver effects of drug candidates from their chemical structures is critical to help guide experimental... |
|
|
Translating clinical findings into knowledge in drug safety evaluation--drug induced liver injury prediction system (DILIps).
J. Sci. Ind. Res. 65(10) , 808, (2006) Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) is a significant concern in drug development due to the poor concordance between preclinical and clinical findings of liver toxicity. We hypothesized that the DILI typ... |
|
|
Developing structure-activity relationships for the prediction of hepatotoxicity.
Chem. Res. Toxicol. 23 , 1215-22, (2010) Drug-induced liver injury is a major issue of concern and has led to the withdrawal of a significant number of marketed drugs. An understanding of structure-activity relationships (SARs) of chemicals ... |
| MFCD00210213 |
| 2-Benzothiazolamine, 6-(trifluoromethoxy)- |
| 2-Amino-6-(trifluoromethoxy)benzothiazole |
| 6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-1,3-benzothiazol-2-amine |
| Riluzole |
| 2-Amino-6-trifluoro methoxy benzothiazole |
| 2-Amino-6-trifluoromethoxybenzothiazole |
| 6-(Trifluoromethoxy)-2-benzothiazolamine |
| Rilutek |
| 6-(Trifluoromethoxy)benzo[d]thiazol-2-amine |

![2-HYDRAZONO-6-(TRIFLUOROMETHOXY)-2,3-DIHYDROBENZO[D]THIAZOLE structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/221/133840-98-9.png)
 CAS#:133840-96-7
CAS#:133840-96-7