Nicotinic acid riboside
Modify Date: 2025-08-26 12:47:31
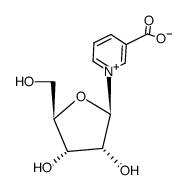
Nicotinic acid riboside structure
|
Common Name | Nicotinic acid riboside | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 17720-18-2 | Molecular Weight | 255.22 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Nicotinic acid ribosideNicotinic acid riboside is a NAD+ precursor in human cells. Nicotinic acid riboside is an authentic intermediate of human NAD+ metabolism[1][2]. |
| Name | NARH-oxidized form |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Nicotinic acid riboside is a NAD+ precursor in human cells. Nicotinic acid riboside is an authentic intermediate of human NAD+ metabolism[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Nicotinic acid riboside (HepG2 cells; 0.01 nM~0.1 mM) helps FK866-treated cells to maintain viability at low micromolar concentrations[1]. .Nicotinic acid riboside formation and release are caused by overexpression of FLAG-tagged CN-II and CN-III in HEK293 and HepG2 cells. CN-II and CN-III generate Nicotinic acid riboside in vitro by dephosphorylation of nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NAMN)[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C11H13NO6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 255.22 |
| Exact Mass | 255.07400 |
| PSA | 113.93000 |
| InChIKey | PUEDDPCUCPRQNY-ZYUZMQFOSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C([O-])c1ccc[n+](C2OC(CO)C(O)C2O)c1 |
| Nicotinic Acid Riboside |