| Description |
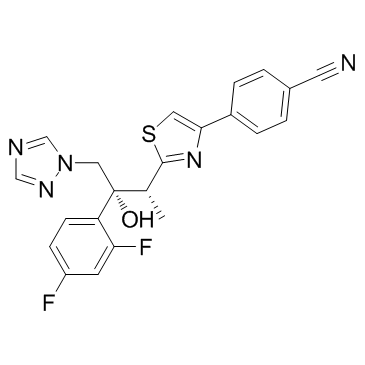
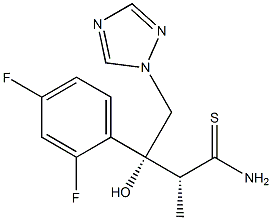
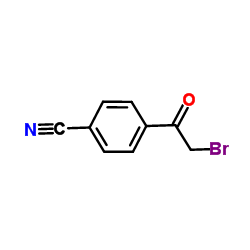
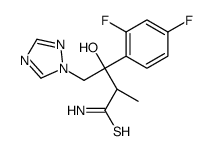
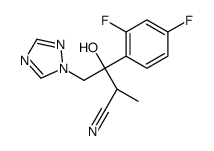
Ravuconazole (BMS-207147;ER-30346) is an orally available triazoleantifungle agent that potently inhibits a wide range of fungi.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
Fungal[1]
|
| In Vitro |
Ravuconazole shows a broad spectrum of activity against a wide range of fungi covering Candida spp., Trichosporon beigelii, C. neoformans and A. fumigatus. The MIC90 ranges from 0.025 to 0.39 mg/mL.Ravuconazoleshows relatively higher levels of activity against three strains of Candida krusei, with MICs ranging from 0.05 to 0.39 mg/mL.Ravuconazoleshows good activity against T. mentagrophytes, T. rubrum, M. gypseum and M. caniswith MICs ranging from 0.05 to 0.39 mg/mL[1]. Ravuconazoleis about two- to four fold more potent than itraconazole and about 40-fold more active than fluconazole against yeasts. Ravuconazoleand itraconazoleare inhibitory to most aspergilli, and against half of the isolates, the activity iscidal. Ravuconazoleand itraconazoleare active, though not cidal, against most hyaline Hyphomycetes, dermatophytes, and the dematiaceous fungi and inactive against Sporothrix schenckii and zygomycetes[2].
|
| In Vivo |
The maximum concentration of ravuconazole in plasma and the area under the concentration-time curve for ravuconazoleshow good linearity over a range of doses from 2 to 40 mg/kg of body weight. Ravuconazole at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg delays mortality significantly compared with the control treatment.Ravuconazole also shows a substantial therapeutic effect against systemic cryptococcosis[1]. Ravuconazole reduces the numbers of CFU in the lungs significantly compared with the numbers of CFU in the lungs of the controls. In an experimental model of oral candidiasis in rats, ravuconazole reduces the numbers of CFU in oral swabs significantly compared with the numbers of CFU in oral swabs from the controls and is more effective than itraconazole and as effective as fluconazole.[3].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mouse[1] Ravuconazole is prepared in 10% DMSO in 0.5% CMC.C. neoformans No. 3 is grown on an SDA plate at 30°Cfor 48 h, and challenge organisms are prepared in sterile saline. Mice (age, 5 weeks; n 5 10) are infected via the tail vein. Ravuconazole are orally administered, in a volume of 0.2 mL per dose, twice daily for 5 consecutive days starting 1 h after infection. Controls receive 10% DMSO in 0.5% CMC. Ravuconazole are administered at doses of 8 and 32 mg/kg. Mortality is recorded daily for 21 days of infection. Drug efficacy is assessed by determining the delay in mortality. Rats[3] The rats are orally infected three times at 48-h intervals with 0.1 mL of a saline suspension containing cells of C. albicansE81022. Ravuconazoleis orally administered, in a volume of 0.5 mL per dose, once daily for 3 consecutive days starting 2 days after the last infection. Control groups receive 10% DMSO in 0.5% CMC. Drugs are administered at doses of 1 and 4 mg/kg. Drug efficacy is assessed 5 days after the last infection by measuring the number of C. albicansorganisms in oral swabs.
|
| References |
[1]. Hata K, et al. In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of ER-30346, a novel oral triazole with a broad antifungal spectrum.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996 Oct;40(10):2237-42. [2]. Fung-Tomc JC, et al. In vitro activity of a new oral triazole, BMS-207147 (ER-30346)Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998 Feb;42(2):313-8. [3]. Hata K, et al. Efficacy of ER-30346, a novel oral triazole antifungal agent, in experimental models of aspergillosis, candidiasis, and cryptococcosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996 Oct;40(10):2243-7.
|