| Description |
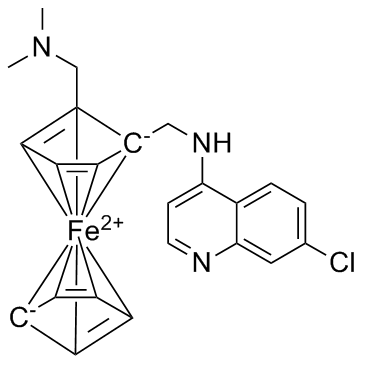
Ferroquine is an ingenious antimalarial agent.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
antimalarial[1]
|
| In Vitro |
The 24 hours post-incubation all newly transformed schistosomula (NTS) exposed to 33.3 µM Ferroquine (FQ), hydroxyl-ferroquine (FQ-OH) and Ruthenoquine (RQ) shows strongly reduced viabilities. 72 hours post-incubation all NTS exposed to 33.3 µM RQ have died, while Ferroquine and FQ-OH treated worms are strongly affected but still alive[1].
|
| In Vivo |
Treatment of mice with 200 and 800 mg/kg Ferroquine, shows low total worm burden reductions of 19.4% and 35.6%. One of the mice treated with 800 mg/kg Ferroquine died within 24 hours post-treatment. No activity is observed treating mice with RQ at 200 mg/kg. Finally, a total worm burden reduction of 17.3% is observed following treatment with FQ-OH. Hence, modification of Chloroquine (CQ) by a ferrocenyl or ruthenocenyl fragment does not increase the antischistosomal properties of CQ. For comparison, at 200 mg/kg mefloquine (MQ) achieves a much higher worm burden reduction of 72.3% in S. mansoni-infected mice. A higher effect against female adult S. mansoni is also observed in MQ treated mice pointing to a sex-specific interference of these drugs with the target. Furthermore, in one of the FQ-OH treated mice many dead worms are recovered and a hepatic shift (i.e. worms migrating to the liver) observed. Hence, Ferroquine and FQ-OH show weak antischistosomal activity in vivo[1].
|
| Cell Assay |
Cytotoxicity studies are performed on human cervix HeLa cancer cells and non tumorigenic human fetal lung fibroblasts MRC-5 to compare the activity of Ferroquine, RQ, FQ-OH, CQ, MQ and Cisplatin. The cell viability is determined via a colorimetric cell-based assay using Resazurin. Briefly, one day before treatment cells are plated in triplicates in 96-well plates at a density of 4 × 103 cells/well in 100 µL. Upon treating cells with increasing concentrations of the target complexes (freshly prepared stock solution in DMSO), cells are incubated at 37°C/6% CO2 for 48 h, the medium is removed, and 100 µL of complete medium containing resazurin (0.2 mg/mL final concentration) is added. After 4 h of incubation at 37°C/6% CO2, the fluorescence of the highly red fluorescent resorufin product is quantified at 590 nm emission with 540 nm excitation wavelength in a SpectraMax M5 microplate Reader[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice[1] Groups of 3-4 NMRI mice are treated orally with single oral doses of 200 mg/kg of Ferroquine, FQ-OH and RQ. In addition, one group of mice is treated with a single oral dose of 800 mg/kg Ferroquine. Untreated mice serve as controls in all experiments. At 21 d post-treatment, animals are killed by the CO2 method and dissected. Worms are removed by picking, then sexed and counted.
|
| References |
[1]. Keiser J, et al. In vitro and in vivo antischistosomal activity of ferroquine derivatives. Parasit Vectors. 2014 Sep 4;7:424.
|