trans-Cinnamonitrile
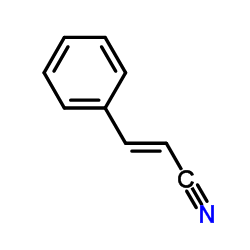
trans-Cinnamonitrile structure
|
Common Name | trans-Cinnamonitrile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1885-38-7 | Molecular Weight | 129.159 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 263.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7N | Melting Point | 18-20 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 105.2±11.2 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | Cinnamonitrile |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 263.8±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 18-20 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7N |
| Molecular Weight | 129.159 |
| Flash Point | 105.2±11.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 129.057846 |
| PSA | 23.79000 |
| LogP | 2.32 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.595 |
| InChIKey | ZWKNLRXFUTWSOY-QPJJXVBHSA-N |
| SMILES | N#CC=Cc1ccccc1 |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | 3276 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | UD1440000 |
| Packaging Group | I; II; III |
| Hazard Class | 6.1 |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2926909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS:2926909090 other nitrile-function compounds VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
The spectroscopy and photochemistry of quinioline structural isomers: (E)- and (Z)-phenylvinylnitrile.
J. Chem. Phys. 143 , 074304, (2015) In Titan's atmosphere, photochemical pathways that lead to nitrogen heteroaromatics may incorporate photoisomerization of their structural isomers as a final step. (E)- and (Z)-phenylvinylnitrile ((E)... |
|
|
Reversible targeting of noncatalytic cysteines with chemically tuned electrophiles.
Nat. Chem. Biol. 8 , 471-6, (2012) Targeting noncatalytic cysteine residues with irreversible acrylamide-based inhibitors is a powerful approach for enhancing pharmacological potency and selectivity. Nevertheless, concerns about off-ta... |
|
|
Formation of mercapturic acids from acrylonitrile, crotononitrile, and cinnamonitrile by direct conjugation and via an intermediate oxidation process.
Drug Metab. Dispos. 9(3) , 246-9, (1981) After administration of acrylonitrile, crotononitrile and cinnamonitrile to rats, two types of mercapturic acids were isolated from urine and identified by mass and NMR spectroscopy as N-acetyl-S-(2-c... |
| Cinnamonitrile |
| 3-phenylacrylonitrile |
| EINECS 217-552-5 |
| (E)-3-Phenylacrylonitrile |
| 2-Propenenitrile, 3-phenyl-, (E)- |
| trans-cinnamonitrile |
| trans-3-Phenyl-2-propenenitrile |
| CINNAMALVA |
| (2E)-3-phenylprop-2-enenitrile |
| trans-β-Phenylacrylonitrile |
| cyanostyrene |
| CINNAMYL NITRILE |
| (2E)-3-Phenylacrylonitrile |
| Cinnamonitrile, (E)- |
| STYRYL CYANIDE |
| naMonitrile |
| Cinnamonitril |
| 2-Propenenitrile, 3-phenyl-, (2E)- |
| MFCD00001930 |
| trans-3-Phenylpropenonitrile |
| Ciamonitrile |
| (E)-Cinnamonitrile |
| β-Cyanostyrene |
 CAS#:59336-59-3
CAS#:59336-59-3 CAS#:13372-81-1
CAS#:13372-81-1 CAS#:591-50-4
CAS#:591-50-4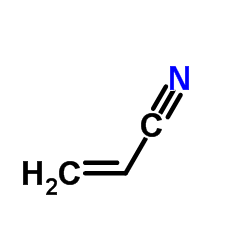 CAS#:107-13-1
CAS#:107-13-1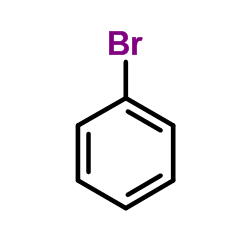 CAS#:108-86-1
CAS#:108-86-1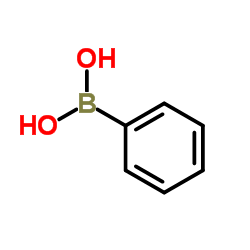 CAS#:98-80-6
CAS#:98-80-6 CAS#:14371-10-9
CAS#:14371-10-9 CAS#:4407-36-7
CAS#:4407-36-7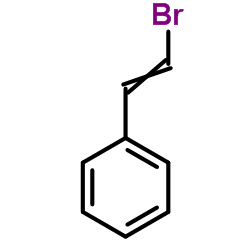 CAS#:103-64-0
CAS#:103-64-0 CAS#:21953-95-7
CAS#:21953-95-7 CAS#:20127-49-5
CAS#:20127-49-5 CAS#:22101-21-9
CAS#:22101-21-9 CAS#:122-97-4
CAS#:122-97-4 CAS#:3531-24-6
CAS#:3531-24-6 CAS#:645-59-0
CAS#:645-59-0 CAS#:2038-57-5
CAS#:2038-57-5 CAS#:4335-60-8
CAS#:4335-60-8 CAS#:1132799-51-9
CAS#:1132799-51-9 CAS#:18891-12-8
CAS#:18891-12-8
