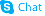Orexin B (human) trifluoroacetate salt
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 18:23:55

Orexin B (human) trifluoroacetate salt structure
|
Common Name | Orexin B (human) trifluoroacetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 205640-91-1 | Molecular Weight | 2899.338 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C123H212N44O35S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Orexin B (human) trifluoroacetate saltOrexin B, human is an endogenous agonist at Orexin receptor with Kis of 420 and 36 nM for OX1 and OX2, respectively. |
| Name | Orexin B(human) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Orexin B, human is an endogenous agonist at Orexin receptor with Kis of 420 and 36 nM for OX1 and OX2, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ki: 420 nM (OX1), 36 nM (OX2)[1] |
| In Vitro | Orexin B is derived by proteolytic amino acid precursor, prepro-orexin, which is encoded by a gene localized to chromosome 17q21 in humans. In radioligand binding studies, Orexin B has a higher affinity for the OX2 receptor[1]. Human Orexin B has two amino acid substitutions when compared with the rodent sequence. OX2 receptor is indeed a high-affinity receptor for human orexin B, with an IC50 of 36 nM in the binding assay and an EC50 of 60 nM in the [Ca2+]i transient assay. Human Orexin B has significantly lower affinity for the human OX1: the calculated IC50 in the competitive binding assay and the EC50 in the [Ca2+]i transient assay are 420 nM and 2500 nM for human orexin-B, respectively[2]. |
| In Vivo | Human Orexin B significantly augments food intake; at the 2 hr time point, 5- and 12-fold stimulation of food consumption is observed by 3 nM and 30 nM orexin-B, respectively[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[2] 3 nM and 30 nM of synthetic human Orexin B is administered in a 5 mL bolus through a catheter placed in the left lateral ventricle of Male Wistar rats (180–200 g) in early light phase. Cumulative food consumption is observed and plotted over the period of 4 hr after injection[2]. |
| References |
[1]. Smart D, et al. Orexins: a new family of neuropeptides. Br J Anaesth. 1999 Nov;83(5):695-7. |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C123H212N44O35S |
| Molecular Weight | 2899.338 |
| Exact Mass | 2897.588135 |
| LogP | -9.29 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.665 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|
| L-Methioninamide, L-arginyl-L-serylglycyl-L-prolyl-L-prolylglycyl-L-leucyl-L-glutaminylglycyl-L-arginyl-L-leucyl-L-glutaminyl-L-arginyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-glutaminyl-L-alanyl-L-serylglycyl-L-asparaginyl-L-histidyl-L-alanyl-L-alanylglycyl-L-isoleucyl-L-leucyl-L-threonyl- |
| L-Arginyl-L-serylglycyl-L-prolyl-L-prolylglycyl-L-leucyl-L-glutaminylglycyl-L-arginyl-L-leucyl-L-glutaminyl-L-arginyl-L-leucyl-L-leucyl-L-glutaminyl-L-alanyl-L-serylglycyl-L-asparaginyl-L-histidyl-L-alanyl-L-alanylglycyl-L-isoleucyl-L-leucyl-L-threonyl-L-methioninamide |
| RSGPPGLQGRLQRLLQASGNHAAGILTM-NH2 |