Dihydrorhodamine 6G
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 09:53:43
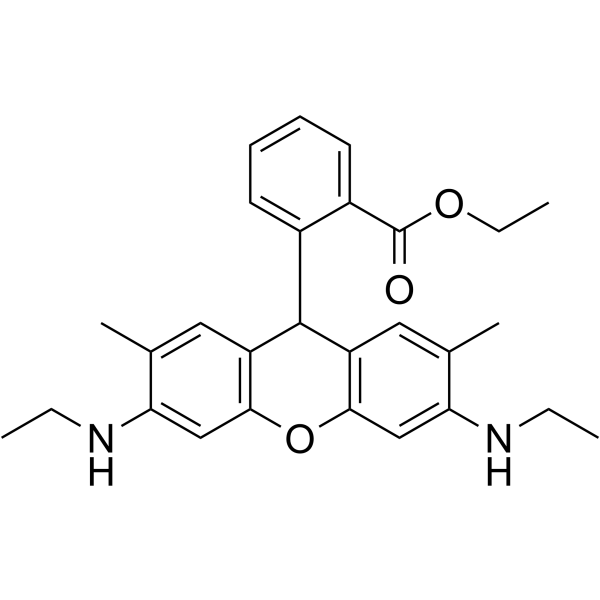
Dihydrorhodamine 6G structure
|
Common Name | Dihydrorhodamine 6G | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 217176-83-5 | Molecular Weight | 444.565 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 572.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 300.0±30.1 °C | |
Use of Dihydrorhodamine 6GDihydrorhodamine 6G (DHR 6G) is the reduced form of Rhodamine 6G, which is used as fluorescent mitochondrial dye. It is nonfluorescent, but it readily enters most of the cells and is oxidized by oxidative species or by cellular redox systems to the fluorescent rhodamine 6G that accumulates in mitochondrial membranes. Dihydrorhodamine 6G is useful for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) including superoxide[1]. |
| Name | DHR 6G [DihydrorhodaMine 6G] |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Dihydrorhodamine 6G (DHR 6G) is the reduced form of Rhodamine 6G, which is used as fluorescent mitochondrial dye. It is nonfluorescent, but it readily enters most of the cells and is oxidized by oxidative species or by cellular redox systems to the fluorescent rhodamine 6G that accumulates in mitochondrial membranes. Dihydrorhodamine 6G is useful for detecting reactive oxygen species (ROS) including superoxide[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 572.4±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H32N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 444.565 |
| Flash Point | 300.0±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 444.241302 |
| LogP | 6.95 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.625 |
| Benzoic acid, 2-[3,6-bis(ethylamino)-2,7-dimethyl-9H-xanthen-9-yl]-, ethyl ester |
| Ethyl 2-[3,6-bis(ethylamino)-2,7-dimethyl-9H-xanthen-9-yl]benzoate |