Cytochalasin C
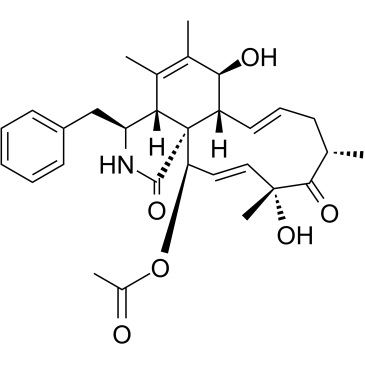
Cytochalasin C structure
|
Common Name | Cytochalasin C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 22144-76-9 | Molecular Weight | 507.618 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 714.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C30H37NO6 | Melting Point | 260-264ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 385.8±32.9 °C | |
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of Cytochalasin CCytochalasin C is a cell-permeable fungal toxin and induces the formation of nuclear rodlets. Cytochalasin C is 10 times less toxic in mice than is cytochalasin D[1][2][3]. |
| Name | cytochalasin c |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cytochalasin C is a cell-permeable fungal toxin and induces the formation of nuclear rodlets. Cytochalasin C is 10 times less toxic in mice than is cytochalasin D[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 714.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 260-264ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C30H37NO6 |
| Molecular Weight | 507.618 |
| Flash Point | 385.8±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 507.262085 |
| PSA | 112.93000 |
| LogP | 2.81 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.602 |
| InChIKey | NAIODHJWOHMDJX-WISUYLHISA-N |
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC1C=CC(C)(O)C(=O)C(C)CC=CC2C(O)C(C)=C(C)C3C(Cc4ccccc4)NC(=O)C123 |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Water Solubility | methylene chloride: 5 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 + H310 + H330-H361 |
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P284-P301 + P310-P302 + P350 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | T+: Very toxic;T: Toxic; |
| Risk Phrases | 26/27/28-63 |
| Safety Phrases | 28-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 1544 6.1/PG 2 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | HA5300500 |
| Packaging Group | I |
| Hazard Class | 6.1(a) |
|
Structure of cytochalasins and cytochalasin B binding sites in human erythrocyte membranes.
Biochemistry 19 , 679, (1980) Twenty cytochalasins were tested for binding to and for inhibition of glucose transport in human erythrocyte membrane. In this membrane three cytochalasin B (CB) binding sites have been identified. Al... |
|
|
Phenotype modulation in primary cultures of rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Effects of drugs that interfere with the functions of the vacuolar system and the cytoskeleton.
Virchows Arch.,. B, Cell Pathol. 59(1) , 1-10, (1990) The transition of adult rat aortic smooth muscle cells from a contractile to a synthetic phenotype during the first week of primary culture on a substrate of fibronectin in serum-free medium was studi... |
|
|
Cytoskeleton regulates expression of genes for transforming growth factor-beta 1 and extracellular matrix proteins in dermal fibroblasts.
J. Cell Physiol. 172(2) , 192-9, (1997) Cytoskeleton not only controls cell morphology but also regulates cell growth, migration, differentiation, and gene expression, events which are fundamental to embryogenesis, carcinogenesis, and wound... |
| 1H-Cycloundec[d]isoindole-1,11(2H)-dione, 15-(acetyloxy)-3,3a,6,6a,9,10,12,15-octahydro-6,12-dihydroxy-4,5,10,12-tetramethyl-3-(phenylmethyl)-, (7Z,13E)- |
| Acétate de (7Z,13E)-3-benzyl-6,12-dihydroxy-4,5,10,12-tétraméthyl-1,11-dioxo-2,3,3a,6,6a,9,10,11,12,15-décahydro-1H-cycloundéca[d]isoindol-15-yle |
| EINECS 244-803-6 |
| (7Z,13E)-3-Benzyl-6,12-dihydroxy-4,5,10,12-tetramethyl-1,11-dioxo-2,3,3a,6,6a,9,10,11,12,15-decahydro-1H-cycloundeca[d]isoindol-15-ylacetat |
| (7Z,13E)-3-Benzyl-6,12-dihydroxy-4,5,10,12-tetramethyl-1,11-dioxo-2,3,3a,6,6a,9,10,11,12,15-decahydro-1H-cycloundeca[d]isoindol-15-yl acetate |
| Cytochalasin C from Metarrhizium anisopliae |
| MFCD00066080 |

