BEC hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 16:51:41
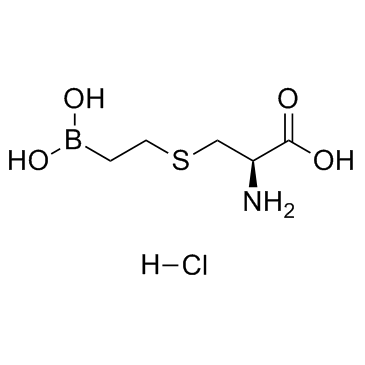
BEC hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | BEC hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 222638-67-7 | Molecular Weight | 229.49000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13BClNO4S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of BEC hydrochlorideBEC HCl is a slow-binding and competitive Arginase II inhibitor with Ki of 0.31 μM (ph 7.5).target: Arginase II [1];In vitro: BEC HCl causes significant enhancement of NO-dependent smooth muscle relaxation in this tissue. [2] BEC HCl enhances perivascular and peribronchiolar lung inflammation, mucus metaplasia, NF-κB DNA binding, and mRNA expression of the NF-κB-driven chemokine genes CCL20 and KC, and lead to further increases in airways hyperresponsiveness. [3] In vivo: BEC HCl increased contractility in isolated myocytes from WT and NOS3 but not NOS1 knockout mice. [4] |
| Name | s-(2-boronoethyl)-l-cysteine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | BEC HCl is a slow-binding and competitive Arginase II inhibitor with Ki of 0.31 μM (ph 7.5).target: Arginase II [1];In vitro: BEC HCl causes significant enhancement of NO-dependent smooth muscle relaxation in this tissue. [2] BEC HCl enhances perivascular and peribronchiolar lung inflammation, mucus metaplasia, NF-κB DNA binding, and mRNA expression of the NF-κB-driven chemokine genes CCL20 and KC, and lead to further increases in airways hyperresponsiveness. [3] In vivo: BEC HCl increased contractility in isolated myocytes from WT and NOS3 but not NOS1 knockout mice. [4] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C5H13BClNO4S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 229.49000 |
| Exact Mass | 229.03500 |
| PSA | 129.08000 |
| LogP | 0.10660 |
| InChIKey | GHPYJLCQYMAXGG-WCCKRBBISA-N |
| SMILES | Cl.NC(CSCCB(O)O)C(=O)O |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| BEC HCl |
| BEC hydrochloride |