5-Phenylvaleric acid

5-Phenylvaleric acid structure
|
Common Name | 5-Phenylvaleric acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 2270-20-4 | Molecular Weight | 178.228 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 308.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H14O2 | Melting Point | 58-60 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 227.2±17.2 °C | |
Use of 5-Phenylvaleric acid5-Phenylvaleric acid (5-Phenylpentanoic acid) is a pentanoic acid of bacterial origin, occasionally found in human biofluids. |
| Name | 5-phenylpentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | 5-Phenylvaleric acid (5-Phenylpentanoic acid) is a pentanoic acid of bacterial origin, occasionally found in human biofluids. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 308.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 58-60 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C11H14O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 178.228 |
| Flash Point | 227.2±17.2 °C |
| Exact Mass | 178.099380 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 2.70 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.528 |
| InChIKey | BYHDDXPKOZIZRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCCCc1ccccc1 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YV7816000 |
| HS Code | 29163900 |
| Precursor 10 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Dietary supplementation with cocoa flavanols does not alter colon tissue profiles of native flavanols and their microbial metabolites established during habitual dietary exposure in C57BL/6J mice.
J. Agric. Food Chem. 62(46) , 11190-9, (2014) Metabolism of flavanols (catechins, procyanidins) by gut microbiota has been extensively characterized. Comparatively little is known about accumulation of flavanols and their metabolites in the colon... |
|
|
Phenylvaleric acid and flavonoid glycosides from Polygonum salicifolium.
J. Nat. Prod. 62(8) , 1101-5, (1999) (3R)-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyloxy-5-phenylvaleric acid (1), (3R)-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyloxy-5-phenylvaleric acid n-butyl ester (2), and a new dihydrochalcone diglycoside 4'-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1--... |
|
|
Metabolism of dietary procyanidins in rats.
Free Radic. Biol. Med. 35(8) , 837-44, (2003) Procyanidins are major dietary polyphenols made of elementary flavan-3-ol (epi)catechin units. They have antioxidant properties and may contribute to health benefits in humans, but little is known abo... |
| 5-Phenylpentanoic acid |
| Ph(CH2)4COOH |
| 5-(phenyl)valeric acid |
| Valeric acid,5-phenyl |
| 5-Phenylvalerate |
| Phenylpentanoic acid |
| 5-Phenyl-pentanoic acid |
| Benzenepentanoic acid |
| Phenylvaleric acid |
| EINECS 218-872-8 |
| 5-Phenyl Valeric acid |
| 5-Phenylvaleric acid |
| 5-phenyl-n-valeric acid |
| MFCD00004416 |
 CAS#:313058-73-0
CAS#:313058-73-0 CAS#:28010-12-0
CAS#:28010-12-0 CAS#:1552-94-9
CAS#:1552-94-9 CAS#:17376-04-4
CAS#:17376-04-4 CAS#:79-10-7
CAS#:79-10-7 CAS#:1501-05-9
CAS#:1501-05-9 CAS#:104-53-0
CAS#:104-53-0 CAS#:2033-24-1
CAS#:2033-24-1 CAS#:17920-83-1
CAS#:17920-83-1 CAS#:78905-97-2
CAS#:78905-97-2 CAS#:109398-68-7
CAS#:109398-68-7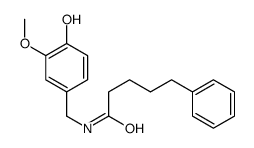 CAS#:105026-92-4
CAS#:105026-92-4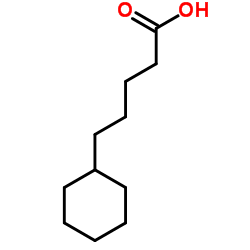 CAS#:5962-88-9
CAS#:5962-88-9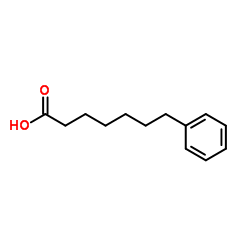 CAS#:40228-90-8
CAS#:40228-90-8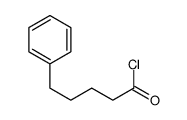 CAS#:20371-41-9
CAS#:20371-41-9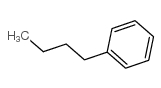 CAS#:104-51-8
CAS#:104-51-8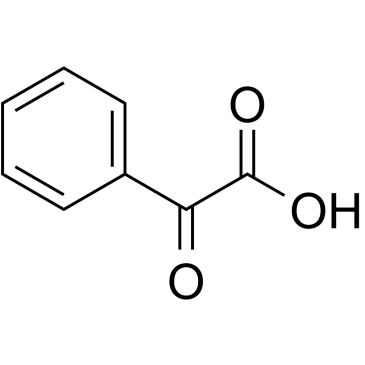 CAS#:611-73-4
CAS#:611-73-4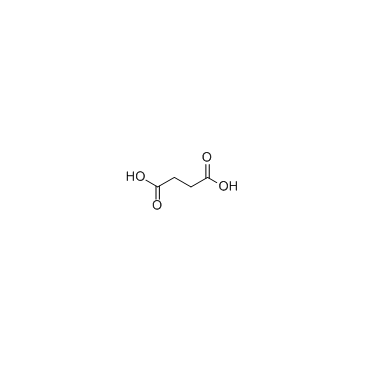 CAS#:110-15-6
CAS#:110-15-6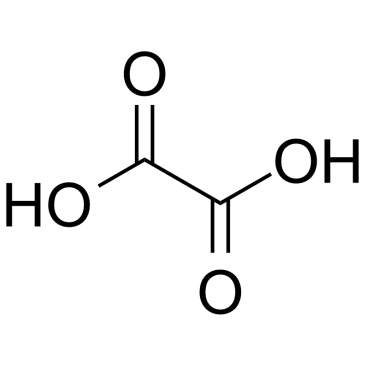 CAS#:144-62-7
CAS#:144-62-7 CAS#:65-85-0
CAS#:65-85-0
