L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate
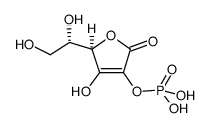
L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate structure
|
Common Name | L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 23313-12-4 | Molecular Weight | 256.10400 | |
| Density | 2.01 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 561.3ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9O9P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 293.2ºC | |
Use of L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphateL-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid) is a long-acting vitamin C derivative that can stimulate collagen formation and expression[1]. L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid) can be used as a culture medium supplement for the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells (hASCs). L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate increases alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and expression of runx2A in hASCs during the osteogenic differentiation[2][3]. |
| Name | [2-(1,2-dihydroxyethyl)-3-hydroxy-5-oxo-2H-furan-4-yl] dihydrogen phosphate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid) is a long-acting vitamin C derivative that can stimulate collagen formation and expression[1]. L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (2-Phospho-L-ascorbic acid) can be used as a culture medium supplement for the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells (hASCs). L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate increases alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and expression of runx2A in hASCs during the osteogenic differentiation[2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: alkaline phosphatase (ALP); collagen formation; runx2A[2][3] |
| In Vitro | L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (0.1-1.5 mM; 2 to 3 weeks with medium exchange every 2 to 3 days) significantly stimulates cell growth, whereas addition of l-Ascorbic acid (Asc) achieves only weak growth stimulation. A combination of Asc-2P and bFGF significantly increases cell growth, but supplementation with EGF and/or insulin does not have any additional effect [1]. L-Ascorbic acid 2-phosphate (50 µM-250 µM) is needed for the effective osteogenic differentiation of human adipose stem cells (hASCs), and higher concentrations of AsA2-P results in increased runx2 expression and ALP activity. The highest proliferation, ALP activity and runx2 expression is achieved with 150 µM AsA2-P and 10 nM dexamethasone (Dex), and 250 µM AsA2-P and 5 nM Dex[3]. Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Line: Human corneal endothelial cells (HCECs) Concentration: 0.1 mM; 0.3 mM; 1.5 mM Incubation Time: 2 to 3 weeks with medium exchange every 2 to 3 days Result: Stimulated HCEC cells growth. |
| References |
| Density | 2.01 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 561.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C6H9O9P |
| Molecular Weight | 256.10400 |
| Flash Point | 293.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 255.99800 |
| PSA | 163.56000 |
| Vapour Pressure | 6.19E-15mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.629 |
|
~% 
L-Ascorbic acid... CAS#:23313-12-4 |
| Literature: Maruyama, Akihiko; Koizumi, Satoshi; Fujio, Tatsuro Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 1990 , vol. 54, # 9 p. 2309 - 2313 |
|
~% 
L-Ascorbic acid... CAS#:23313-12-4 |
| Literature: Nomura, Hiroaki; Nakamichi, Hideo; Wada, Yoshikazu Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1982 , vol. 30, # 3 p. 1024 - 1029 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |
| Ascorbate-2-phosphate |
| 2-phospho-L-ascorbic acid |
| 2-O-phosphonohex-1-enofuranos-3-ulose |
| L-Ascorbate 2-monophosphate |
| ascorbic acid-2-phosphoric acid ester |
| L-ascorbic acid 2-O-phosphate |
| ascorbic acid 2-phosphate |