| Description |
Befetupitant is a high-affinity, nonpeptide, competitive tachykinin 1 receptor (NK1R) antagonist.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
NK1R[1]
|
| In Vivo |
Befetupitant, a different, highly selective NK1R antagonist, is tested in the alkali burn model. Topical application of Befetupitant for 4 days is effective (P<0.05) in reducing hemangiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis at both concentrations (0.4 and 1.6 mg/mL). Befetupitant and its vehicle DMSO, however, induced corneal opacity even in healthy controls, as observed at slit-lamp examination. Moreover, fluorescein and hematoxylin-eosin staining showed epithelial damage and inflammatory cellular infiltration in the stroma, respectively, confirming DMSO toxicity. Topical application of Befetupitant reduces corneal neovascularization (CNV) in the alkali burn model but is toxic owing to the vehicle (DMSO); hence, Befetupitant is not tested in the suture model[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Mice[1] Female, 6- to 8-week-old, C57BL/6 mice are used for all experiments (total: 283 mice). A corneal alkali burn is created for the Lanepitant experiment. Animals are then randomized into three groups (n=6), receiving 10 μL Befetupitant 0.4 or 1.6 mg/mL in 100% DMSO or 10 μL vehicle (DMSO) as control, topically six times a day for 4 days. Topical Befetupitant and DMSO toxicity is evaluated in two groups of six healthy animals receiving in the left eye 10 μL topical Befetupitant 0.4 mg/mL or 100% DMSO, six times a day for 9 days.
|
| References |
[1]. Bignami F, et al. NK1 receptor antagonists as a new treatment for corneal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Sep 16;55(10):6783-94.
|
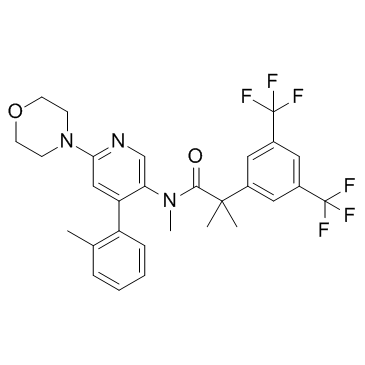
![N-methyl-N-[6-(morpholin-4-yl)-4-(o-tolyl)pyridin-3-yl]amine Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/300/290297-36-8.png) CAS#:290297-36-8
CAS#:290297-36-8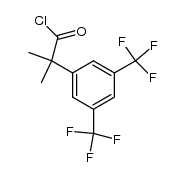 CAS#:289686-69-7
CAS#:289686-69-7 CAS#:342417-04-3
CAS#:342417-04-3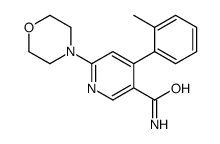 CAS#:342417-06-5
CAS#:342417-06-5 CAS#:342417-05-4
CAS#:342417-05-4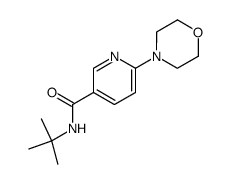 CAS#:881743-66-4
CAS#:881743-66-4 CAS#:342417-03-2
CAS#:342417-03-2![[6-(morpholin-4-yl)-4-(o-tolyl)pyridin-3-yl]carbamic acid methyl ester Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/440/342417-07-6.png) CAS#:342417-07-6
CAS#:342417-07-6 CAS#:342416-86-8
CAS#:342416-86-8 CAS#:328-70-1
CAS#:328-70-1