Ranatensin
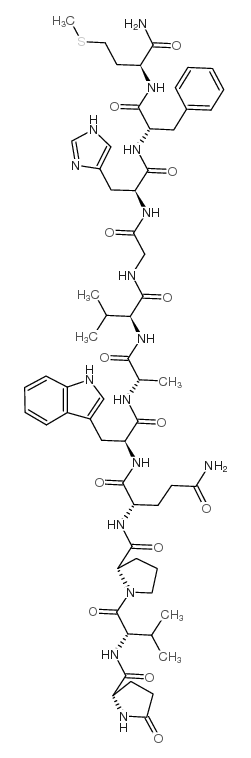
Ranatensin structure
|
Common Name | Ranatensin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 29451-71-6 | Molecular Weight | 1281.48000 | |
| Density | 1.326 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1790.5ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C61H84N16O13S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 1036.6ºC | |
Use of RanatensinRanatensin is a undecapeptide and a Bombesin Receptor angonist, can be isolated from amphibian skin, such as the frog, Rana pipiens. Ranatensin could maintain the dynamic balance of animal blood pressure, without cross-tachyphylaxis with Angiotensin amide (HY-P2212), Bradykinin (HY-P0206), or Norepinephrine (HY-13715)[1][2]. |
| Name | ranatensin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Ranatensin is a undecapeptide and a Bombesin Receptor angonist, can be isolated from amphibian skin, such as the frog, Rana pipiens. Ranatensin could maintain the dynamic balance of animal blood pressure, without cross-tachyphylaxis with Angiotensin amide (HY-P2212), Bradykinin (HY-P0206), or Norepinephrine (HY-13715)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ranatensin (0.3 nM; 30 min) 能够刺激多种胰促分泌物诱导淀粉酶释放[1]。 |
| In Vivo | Ranatesin (10-50 μg/mL, 0.1-1 mL; 静脉注射; 单剂量) 会增加狗和兔子的血压,表明其具有直接的外周血管收缩作用[2]。 Ranatesin (10-50 μg/mL, 0.1-1 mL; 静脉注射; 单剂量) 也能降低猴子的血压,与 Eledoisin (HY-P0006) 一样有效。它对血管平滑肌有直接的外周作用[2]。 Ranatesin (10-50 μg/mL, 0.005-0.1 mL; 静脉注射; 单剂量) 根据大鼠血压的基础水平具有可变的作用,在高水平时显示出降压效果,在低水平时升高血压,产生这一变化的可能原因是外周交感神经末梢释放去甲肾上腺素[2]。 |
| References |
| Density | 1.326 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1790.5ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C61H84N16O13S |
| Molecular Weight | 1281.48000 |
| Flash Point | 1036.6ºC |
| Exact Mass | 1280.61000 |
| PSA | 467.26000 |
| LogP | 3.20430 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.607 |
| InChIKey | AUOCWSNQHWTPIJ-JMYPGRSYSA-N |
| SMILES | CSCCC(NC(=O)C(Cc1ccccc1)NC(=O)C(Cc1cnc[nH]1)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(Cc1c[nH]c2ccccc12)NC(=O)C(CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)C1CCCN1C(=O)C(NC(=O)C1CCC(=O)N1)C(C)C)C(C)C)C(N)=O |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Molecular biology of bombesin-like peptides. Comparison of cDNAs encoding human gastrin-releasing peptide, human neuromedin B, and amphibian ranatensin.
Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 547 , 10-20, (1988)
|
|
|
Bombesin-related peptides induce calcium mobilization in a subset of human small cell lung cancer cell lines.
J. Biol. Chem. 262(34) , 16456-60, (1987) To examine the biochemical basis for growth factor-induced responses in human lung cancer cells, we used the quin2 technique to study the effect of the amphibian peptide bombesin and its congeners inc... |
|
|
Identification of the C-terminal amino acid amides by carboxypeptidase Y digestion and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry.
Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 34(5) , 897-907, (1994) The combination method of carboxypeptidase Y digestion and fast atom bombardment (FAB) mass spectrometry is described for the identification of C-terminal amino acid amides in peptides. Carboxypeptida... |
| 5-Oxo-L-Pro-L-Val-L-Pro-L-Glu(NH2)-L-Trp-L-Ala-L-Val-Gly-L-His-L-Phe-L-Met-NH2 |
| GLP-VAL-PRO-GLN-TRP-ALA-VAL-GLY-HIS-PHE-MET-NH2 |
| pGlu-Val-Pro-Gln-Trp-Ala-Val-Gly-His-Phe-Met-NH2 |
| PYROGLU-VAL-PRO-GLN-TRP-ALA-VAL-GLY-HIS-PHE-MET-NH2 |
| PGLU-VAL-PRO-GLN-TRP-ALA-VAL-GLY-HIS-PHE-MET-NH2 |
| PYR-VAL-PRO-GLN-TRP-ALA-VAL-GLY-HIS-PHE-MET-NH2 |

