TAPS (buffer)
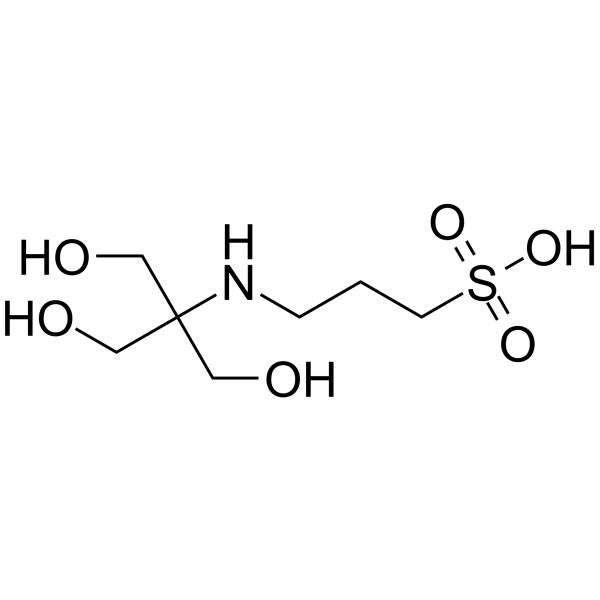
TAPS (buffer) structure
|
Common Name | TAPS (buffer) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 29915-38-6 | Molecular Weight | 243.278 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C7H17NO6S | Melting Point | 230-235 °C (dec.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 110 °C | |
Use of TAPS (buffer)TAPS is a biological buffer, remain lysozyme native structure intact and prevents thermal denaturation against high temperatures. TAPS exhibits pKa value of 8.1, while the half-maximum values of connexin channel activity is 8.5 (pH)[1][2]. |
| Name | 3-[[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]amino]propane-1-sulfonic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | TAPS is a biological buffer, remain lysozyme native structure intact and prevents thermal denaturation against high temperatures. TAPS exhibits pKa value of 8.1, while the half-maximum values of connexin channel activity is 8.5 (pH)[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 230-235 °C (dec.) |
| Molecular Formula | C7H17NO6S |
| Molecular Weight | 243.278 |
| Flash Point | 110 °C |
| Exact Mass | 243.077652 |
| PSA | 135.47000 |
| LogP | -2.40 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.561 |
| InChIKey | YNLCVAQJIKOXER-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=S(=O)(O)CCCNC(CO)(CO)CO |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38:Irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin . |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29221980 |
|
~% 
TAPS (buffer) CAS#:29915-38-6 |
| Literature: Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, , p. 667 - 670 |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 29221980 |
|---|
|
The [NiFe]-Hydrogenase of Pyrococcus furiosus Exhibits a New Type of Oxygen Tolerance.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137 , 13556-65, (2015) We report the first direct electrochemical characterization of the impact of oxygen on the hydrogen oxidation activity of an oxygen-tolerant, group 3, soluble [NiFe]-hydrogenase: hydrogenase I from Py... |
|
|
Towards autotrophic tissue engineering: Photosynthetic gene therapy for regeneration.
Biomaterials 75 , 25-36, (2015) The use of artificial tissues in regenerative medicine is limited due to hypoxia. As a strategy to overcome this drawback, we have shown that photosynthetic biomaterials can produce and provide oxygen... |
|
|
Producing glucose 6-phosphate from cellulosic biomass: structural insights into levoglucosan bioconversion.
J. Biol. Chem. 290 , 26638-48, (2015) The most abundant carbohydrate product of cellulosic biomass pyrolysis is the anhydrosugar levoglucosan (1,6-anhydro-β-d-glucopyranose), which can be converted to glucose 6-phosphate by levoglucosan k... |
| 1-Propanesulfonic acid, 3-[[2-hydroxy-1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)ethyl]amino]- |
| [(2-Hydroxy-1,1-bis(hydroxymethyl)ethyl)amino]-1-propanesulfonic acid |
| 3-((1,3-Dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl)amino)propane-1-sulfonic acid |
| N-Tris(Hydroxymethy)methyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid |
| T3A |
| 3-{[1,3-dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)propan-2-yl]amino}propane-1-sulfonic acid |
| N-Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic Acid [Good's buffer component |
| EINECS 249-954-1 |
| N-[Tris(hydroxymethyl)metyl]-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid |
| 3-(TRIS(HYDROXYMETHYL)METHYLAMINO)-1-PROPANESULFONIC ACID |
| 3-{[1,3-Dihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-2-propanyl]amino}-1-propanesulfonic acid |
| MFCD00007538 |
| TAPS |
| 3-[N-Tris-(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]propanesulphonic (TAPS) |
| N-Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid |