Telatinib
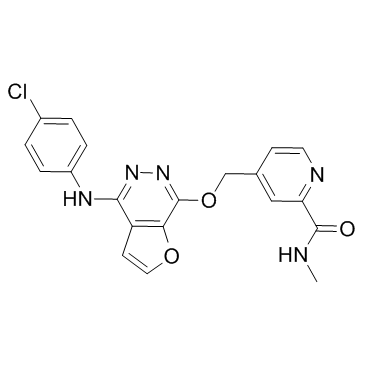
Telatinib structure
|
Common Name | Telatinib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 332012-40-5 | Molecular Weight | 409.826 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 713.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C20H16ClN5O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 385.4±32.9 °C | |
Use of TelatinibTelatinib (Bay 57-9352) is an orally active, small molecule inhibitor of VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFα, and c-Kit with IC50s of 6, 4, 15 and 1 nM, respectively. |
| Name | 4-[[4-(4-chloroanilino)furo[2,3-d]pyridazin-7-yl]oxymethyl]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Telatinib (Bay 57-9352) is an orally active, small molecule inhibitor of VEGFR2, VEGFR3, PDGFα, and c-Kit with IC50s of 6, 4, 15 and 1 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
VEGFR2:6 nM (IC50) VEGFR3:4 nM (IC50) PDGFRα:15 nM (IC50) c-Kit:1 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Telatinib has low affinity for the Raf kinase pathway, epidermal growth factor receptor family, the fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) family, or the Tie-2 receptor[2]. Telatinib is metabolized by various cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms including CYP3A4/3A5, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 as well as by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A4 (UGT1A4), with the formation of the N-glucuronides of telatinib as the major biotransformation pathway in man. In vitro studies show telatinib to be a weak substrate of the adenosine triphosphate binding cassette (ABC) B1 (ABCB1) transporter[3]. Telatinib at 1 μM significantly enhances the intracellular accumulation of [3H]-mitoxantrone (MX) in ABCG2-overexpressing cell lines. In addition, telatinib at 1 μM significantly reduces the rate of [3H]-MX efflux from ABCG2-overexpressing cells. Furthermore, telatinib significantly inhibits ABCG2-mediated transport of [3H]-E217βG in ABCG2 overexpressing membrane vesicles[4]. |
| In Vivo | Telatinib causes a significant decrease in endothelium-dependent and endothelium-independent vasodilation. VEGF inhibition by itself decreases NO synthesis, which promotes vasoconstriction, increases peripheral resistance, and therefore can induce an increase in blood pressure[1]. Telatinib (15 mg/kg) with doxorubicin (1.8 mg/kg) significantly decreases the growth rate and tumor size of ABCG2 overexpressing tumors in a xenograft nude mouse model[4]. |
| Kinase Assay | The vanadate (Vi)-sensitive ATPase activity of ABCG2 in the membrane of High Five insect cells is measured. Briefly, membrane (2 μg/0.06 mL) are incubated in ATPase assay buffer with or without 0.4 mM vanadate at 37°C for 5 min and then incubated with varying concentrations of telatinib at 37°C for 5 min. The ATPase reaction is started by the addition of 4 mM Mg-ATP. After incubating at 37°C for 10 min, the reactions are stopped by adding 0.05 mL of 10% SDS solution. The liberated inorganic phosphate is measured[4]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: The mice are randomized into four groups and treated with one of the following regimens: (a) vehicle (10% N-methyl-pyrrolidinone, 90% polyethylene glycol 300) (q3d×6), (b) DOX (1.8 mg/kg, i.p., q3d×6), (c) telatinib dissolved in 10% N-methyl-pyrrolidinone, 90% polyethylene glycol 300 (15 mg/kg, p.o., every 2nd and 3rd day; total 12 times), and (d) DOX (1.8 mg/kg, i.p., q3d×6) + telatinib (15 mg/kg, p.o., every 2nd and 3rd day, given 1 h before giving DOX; total 12 times). DOX for injection is prepared by dissolving in saline. Tumor volume is measured using calipers and body weights are recorded[4]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 713.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C20H16ClN5O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 409.826 |
| Flash Point | 385.4±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 409.094177 |
| PSA | 102.17000 |
| LogP | 2.53 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.684 |
| InChIKey | QFCXANHHBCGMAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CNC(=O)c1cc(COc2nnc(Nc3ccc(Cl)cc3)c3ccoc23)ccn1 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
|
~45% 
Telatinib CAS#:332012-40-5 |
| Literature: BAYER CORPORATION Patent: EP1228063 B1, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 45-46 ; |
|
~46% 
Telatinib CAS#:332012-40-5 |
| Literature: Bayer Pharmaceuticals Corporation Patent: US6689883 B1, 2004 ; Location in patent: Page column 61 ; |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| Telatinib,BAY 57-9352,BAY 57-9352 |
| 4-(4-(4-chloro-phenylamino)-furo[2,3-d]pyridazin-7-yloxymethyl)-pyridine-2-carboxylic acid methylamide |
| S2231_Selleck |
| BAY57-9352 |
| Telatinib |
| 4-[({4-[(4-Chlorophenyl)amino]furo[2,3-d]pyridazin-7-yl}oxy)methyl]-N-methyl-2-pyridinecarboxamide |
| Bay 57-9352 |
| UNII:18P7197Q7J |
| 4-(4-chlorophenylamino)-7-(2-methylaminocarbonyl-4-pyridylmethoxy)furo-[2,3-d]pyridazine |
| 4-((4-(4-chlorophenylamino)furo[2,3-d]pyridazin-7-yloxy)methyl)-N-methylpicolinamide |
| 2-Pyridinecarboxamide, 4-[[[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)amino]furo[2,3-d]pyridazin-7-yl]oxy]methyl]-N-methyl- |
| BAY-579352 |
![4-chloro-N-(4-chlorophenyl)furo[2,3-d]pyridazin-7-amine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/494/332013-41-9.png)
![7-chloro-4-[N-(4-chlorophenyl)amino]-[2,3-d]furopyridazine structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/032/332013-40-8.png)