3,6-Dichloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acid
Modify Date: 2024-01-12 11:03:19
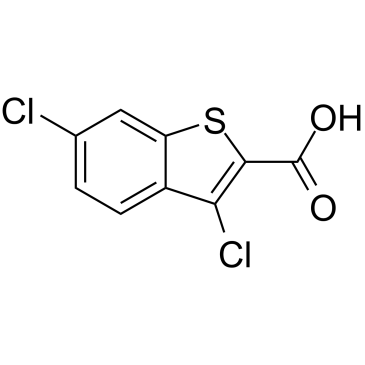
3,6-Dichloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acid structure
|
Common Name | 3,6-Dichloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 34576-94-8 | Molecular Weight | 247.098 | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 426.4±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C9H4Cl2O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 211.7±27.3 °C | |
Use of 3,6-Dichloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acidBT2 is a BCKDC kinase (BDK) inhibitor with an IC50 of 3.19 μM. BT2 binding to BDK triggers helix movements in the N-terminal domain, resulting in the dissociation of BDK from the branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC)[1]. BT2 (compound 4) is also a potent and selective Mcl-1 inhibitor with a Ki value of 59 μM[2]. |
| Name | 3,6-Dichloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | BT2 is a BCKDC kinase (BDK) inhibitor with an IC50 of 3.19 μM. BT2 binding to BDK triggers helix movements in the N-terminal domain, resulting in the dissociation of BDK from the branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC)[1]. BT2 (compound 4) is also a potent and selective Mcl-1 inhibitor with a Ki value of 59 μM[2]. |
|---|---|
| Target |
BDK:3.19 μM (IC50) Mcl-1:59 μM (Ki) |
| In Vivo | BT2 (20 mg/kg/day; intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 7 days; C57BL/6J male mice) treatment robustly enhances BCKDC activity in the heart (12.3-fold) compared with the vehicle-treated animals. Less activation is obtained in muscle and kidney at 3.6- and 3.8-fold, respectively. The -fold activation of BCKDC activity in the above tissues correlates with decreased phosphorylation in heart, muscle, and kidney after the long term BT2 treatment. BT2 treatment reduces the protein levels of BDK in kidneys and heart[1]. Animal Model: C57BL/6J male mice (8-10-week-old)[1] Dosage: 20 mg/kg/day Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; daily; for 1 week Result: BCKDC activity was robustly (12.3-fold) enhanced in the heart compared with the vehicle-treated animals. Less activation was obtained in muscle and kidney at 3.6- and 3.8-fold, respectively. The protein levels of BDK in kidneys and heart were reduced to averages of 39 and 24%, respectively. |
| References |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 426.4±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C9H4Cl2O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 247.098 |
| Flash Point | 211.7±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 245.930908 |
| PSA | 65.54000 |
| LogP | 4.65 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.723 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|
| HS Code | 2934999090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2934999090. other heterocyclic compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
| 3,6-Dichloro-benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid |
| 2-Chlorcarbonyl-3,6-dichlorbenzo<b>thiophen |
| 3,6-Dichlorbenzo<b>thiophen-2-carbonsaeure |
| 3,6-Dichloro-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxylic acid |
| Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid, 3,6-dichloro- |
| 3,6-Dichlor-benzo-<b>-thiophen-2-carbonsaeurechlorid |