Zinc Trifluoromethanesulfinate
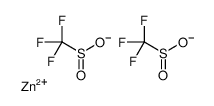
Zinc Trifluoromethanesulfinate structure
|
Common Name | Zinc Trifluoromethanesulfinate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 39971-65-8 | Molecular Weight | 331.51900 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C2F6O4S2Zn | Melting Point | 157 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Zinc bis(trifluoromethanesulfinate) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Melting Point | 157 °C |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C2F6O4S2Zn |
| Molecular Weight | 331.51900 |
| Exact Mass | 329.84300 |
| PSA | 118.68000 |
| LogP | 2.49950 |
| InChIKey | UANOWFITUWBPCF-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| SMILES | O=S([O-])C(F)(F)F.O=S([O-])C(F)(F)F.[Zn+2] |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H318-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 9 | |
|
Practical and innate carbon-hydrogen functionalization of heterocycles.
Nature 492 , 95-100, (2012) Nitrogen-rich heterocyclic compounds have had a profound effect on human health because these chemical motifs are found in a large number of drugs used to combat a broad range of diseases and pathophy... |
|
|
Radical-based regioselective C-H functionalization of electron-deficient heteroarenes: scope, tunability, and predictability.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135 , 12122-12134, (2013) Radical addition processes can be ideally suited for the direct functionalization of heteroaromatic bases, yet these processes are only sparsely used due to the perception of poor or unreliable contro... |
| Zinc trifluoromethanesulfinate |
| Bis(trifluoromethanesulfinic Acid) Zinc(II) Salt Dihydrate |
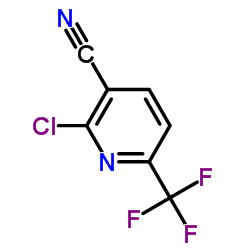 CAS#:386704-06-9
CAS#:386704-06-9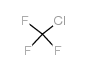 CAS#:75-72-9
CAS#:75-72-9 CAS#:679-77-6
CAS#:679-77-6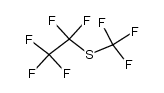 CAS#:33547-10-3
CAS#:33547-10-3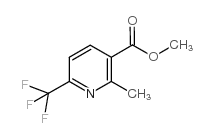 CAS#:205582-88-3
CAS#:205582-88-3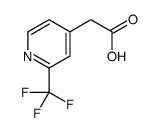 CAS#:1008737-00-5
CAS#:1008737-00-5 CAS#:1214351-44-6
CAS#:1214351-44-6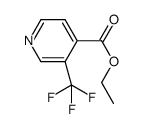 CAS#:1214337-41-3
CAS#:1214337-41-3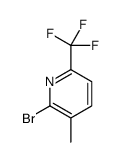 CAS#:1211525-93-7
CAS#:1211525-93-7
