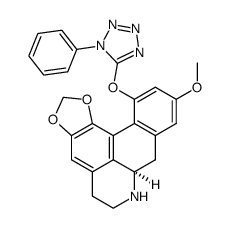
Xylopine
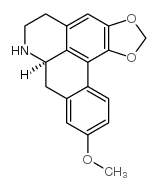
Xylopine structure
|
Common Name | Xylopine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 517-71-5 | Molecular Weight | 295.33200 | |
| Density | 1.289g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 483.4ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H17NO3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 193.7ºC | |
Use of XylopineXylopine is an aporphine alkaloid with cytotoxic activity on cancer cells. Xylopine induces oxidative stress, causes G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells[1]. |
| Name | Xylopine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Xylopine is an aporphine alkaloid with cytotoxic activity on cancer cells. Xylopine induces oxidative stress, causes G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in cancer cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Xylopine (3.5 μM-14 μM; 24-48 hours) displays potent cytotoxicity in a time- and does-depenpent manner[1]. Xylopine (72 h) has cytotoxic activity, with IC50 values ranging from 6.4 to 26.6 μM in eight different cancer cell lines (MCF7, HCT116, HepG2, SCC-9, HSC-3, HL-60, K-562, and B16-F10)[1]. Xylopine (3.5 μM-14 μM; 24-48 hours) causes cell cycle block at the phase G2/M, which is followed by internucleosomal DNA fragmentation[1]. Xylopine (3.5 μM-14 μM; 24-48 hours) significantly increases the early and late apoptosis, induces mitochondrial depolarization, and increases caspase-3 activation[1]. Xylopine also causes an increase in the production of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species (ROS/RNS), including hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide, but not superoxide anion, and reduces glutathione levels are decreased in Xylopine-treated HCT116 cells[1].HCT116 cells[1]3.5 μM, 7 μM, and 14 μM 24 hours, 48 hoursInduced G2/M phase arrest.HCT116 cells[1]3.5 μM, 7 μM, and 14 μM 24 hours, 48 hoursSignificantly increased the early and late apoptosis. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: HCT116 cells Concentration: 3.5 μM, 7 μM, and 14 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours, 48 hours Result: Displayed potent cytotoxicity in HCT116 cells. Cell Cycle Analysis[1] Cell Line: HCT116 cells Concentration: 3.5 μM, 7 μM, and 14 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours, 48 hours Result: Induced G2/M phase arrest. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: HCT116 cells Concentration: 3.5 μM, 7 μM, and 14 μM Incubation Time: 24 hours, 48 hours Result: Significantly increased the early and late apoptosis. |
| References |
| Density | 1.289g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 483.4ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H17NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 295.33200 |
| Flash Point | 193.7ºC |
| Exact Mass | 295.12100 |
| PSA | 39.72000 |
| LogP | 3.16260 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.635 |
| InChIKey | RFWCCZDSXIZJMF-CQSZACIVSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1ccc2c(c1)CC1NCCc3cc4c(c-2c31)OCO4 |
|
~% 
Xylopine CAS#:517-71-5 |
| Literature: Lu, Sheng-Teh; Wu, Yang-Chang; Leou, Shiow-Piaw Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1985 , vol. 24, # 8 p. 1829 - 1834 |
|
~% 
Xylopine CAS#:517-71-5 |
| Literature: Lu, Sheng-Teh; Wu, Yang-Chang; Leou, Shiow-Piaw Phytochemistry (Elsevier), 1985 , vol. 24, # 8 p. 1829 - 1834 |
|
~% 
Xylopine CAS#:517-71-5 |
| Literature: Manske Canadian Journal of Research, Section B: Chemical Sciences, 1938 , vol. 16, p. 85 Chem. Zentralbl., 1938 , vol. 109, # II p. 324 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 6Abeta-noraporphine,9-methoxy-1,2-(methylenedioxy) |
| (7aR)-6,7,7a,8-Tetrahydro-10-methoxy-5H-benzo[g]-1,3-benzodioxolo[6,5,4-de]quinoline |