| Description |
Evodiamine is an alkaloid isolated from the fruit of Evodia rutaecarpa Bentham with diverse biological activities including anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity, and antitumor.
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| In Vitro |
Evodiamine shows cytotoxicity against a variety of human cancer cell-lines by inducing apoptosis. Moreover, it is a naturally multi-targeting antitumor molecule, which exerts the antitumor activity by various molecular mechanism such as caspase-dependent and -independent pathways, sphingomyelin pathway, calcium/JNK signaling, 31 PI3K/Akt/caspase and Fas-L/NF-κB signaling pathways32[1].
|
| In Vivo |
Evodiamine inhibits the metabolism of dapoxetine. Compared to the control group, the pharmacokinetic parameter of t1/2, AUC(0-∞) and Tmax of dapoxetine in evodiamine group is significantly increased by 63.3%, 44.8% and 50.4%, respectively. Moreover, evodiamine has significantly decreased the pharmacokinetic parameter of t1/2 and AUC(0-∞) of desmethyl dapoxetine[2]. Evodiamine suppresses tumor growth in a subcutaneous H22 xenograft model. Evodiamine attenuates VEGF-induced angiogenesis in vivo[3].
|
| Cell Assay |
Evodiamine is dissolved in DMSO and diluted with appropriate medium before use. The evodiamine-inspired new scaffolds are assayed for growth inhibitory activities toward human cancer cell-lines A549 (lung cancer), MDA-MB-435 (breast cancer) and HCT116 (colon cancer) using the MTT assay. Evodiamine and camptithecin are used as reference drugs[1].
|
| Animal Admin |
Rats: Twelve healthy male Sprague-Dawley rats are randomly divided into 2 groups: the control group (received oral 10 mg/kg dapoxetine alone) and the combination group (10 mg/kg dapoxetine orally co-administered with 100 mg/kg evodiamine). The plasma concentration of dapoxetine and desmethyl dapoxetine are estimated by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS), and different pharmacokinetic parameters are calculated[2]. Mice: A nude mouse xenograft model is established by using 4–6-week-old male BALB/c nude mice. Mice are dosed daily with 20 mg/kg (10 mL/kg) of evodiamine intragastrically, six mice are dosed intraperitoneally with 10 mg/kg of 5-flurouracil (5-FU) twice a week, and six mice are not treated. The tumor volumes are determined by measuring two dimensions, with tumor volume=length×width×width/2. After 2 or 3 weeks of treatment, mice are sacrificed by cervical dislocation under anesthesia with ether, and the tumor tissues are collected[3].
|
| References |
[1]. Wang S, et al. Scaffold Diversity Inspired by the Natural Product Evodiamine: Discovery of Highly Potent and Multitargeting Antitumor Agents. J Med Chem. 2015 Aug 27;58(16):6678-96. [2]. Li RF,et al. Effects of Evodiamine on the Pharmacokinetics of Dapoxetine and Its Metabolite Desmethyl Dapoxetine inRats. Pharmacology. 2016;97(1-2):43-7. [3]. Shi L, et al. Evodiamine exerts anti-tumor effects against hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibiting β-catenin-mediated angiogenesis. Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):12791-12803.
|
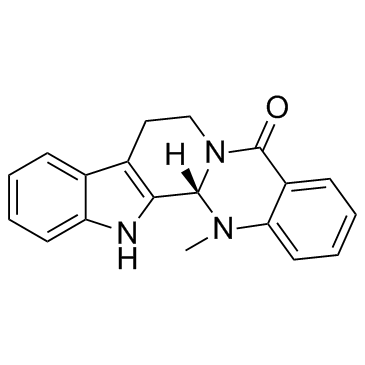
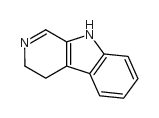 CAS#:4894-26-2
CAS#:4894-26-2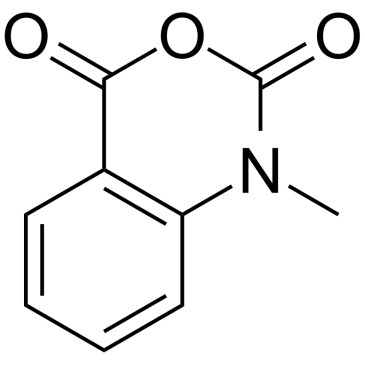 CAS#:10328-92-4
CAS#:10328-92-4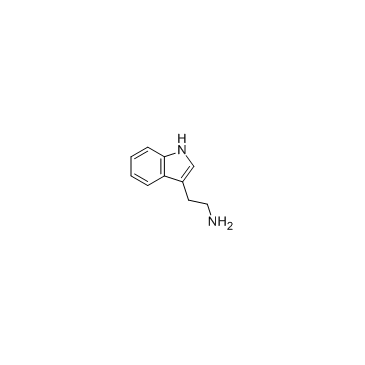 CAS#:61-54-1
CAS#:61-54-1 CAS#:118-48-9
CAS#:118-48-9![2-amino-N-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]benzamide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/413/33284-02-5.png) CAS#:33284-02-5
CAS#:33284-02-5![3-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]quinazolin-4-one Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/446/60941-86-8.png) CAS#:60941-86-8
CAS#:60941-86-8 CAS#:119-68-6
CAS#:119-68-6
