DTNB
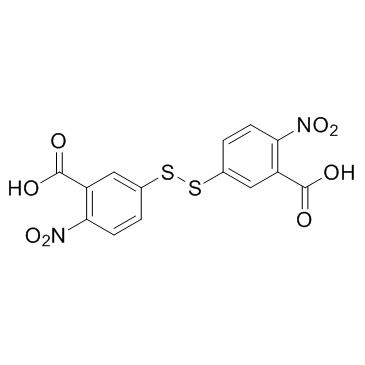
DTNB structure
|
Common Name | DTNB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69-78-3 | Molecular Weight | 396.352 | |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 671.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O8S2 | Melting Point | 240-245 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 360.1±31.5 °C | |
Use of DTNBDTNB(Ellman’s Reag) is a chemical used to quantify the number or concentration of thiol groups in a sample; can be used for measuring low-molecular mass thiols such as glutathione in both pure solutions and biological samples, such as blood. |
| Name | dithionitrobenzoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | DTNB(Ellman’s Reag) is a chemical used to quantify the number or concentration of thiol groups in a sample; can be used for measuring low-molecular mass thiols such as glutathione in both pure solutions and biological samples, such as blood. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 671.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 240-245 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H8N2O8S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.352 |
| Flash Point | 360.1±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 395.972198 |
| PSA | 216.84000 |
| LogP | 3.97 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.769 |
| InChIKey | KIUMMUBSPKGMOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)c1cc(SSc2ccc([N+](=O)[O-])c(C(=O)O)c2)ccc1[N+](=O)[O-] |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong bases, strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | DG9650000 |
| HS Code | 29309070 |
| HS Code | 2930909090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2930909090. other organo-sulphur compounds. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Disturbed Hsp70 and Hsp27 expression and thiol redox status in porcine kidney PK15 cells provoked by individual and combined ochratoxin A and citrinin treatments.
Food Chem. Toxicol. 71 , 97-105, (2014) The aim of this study was to explore the oxidative properties of ochratoxin A (OTA) and citrinin (CTN) as a possible underlying mechanism of their individual and/or combined cytotoxicity. Metabolic ac... |
|
|
Metabolic and tissue-specific regulation of acyl-CoA metabolism.
PLoS ONE 10(3) , e0116587, (2015) Acyl-CoA formation initiates cellular fatty acid metabolism. Acyl-CoAs are generated by the ligation of a fatty acid to Coenzyme A mediated by a large family of acyl-CoA synthetases (ACS). Conversely,... |
|
|
Mitochondrial NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase knockdown inhibits tumorigenicity of melanoma cells.
Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 451(2) , 246-51, (2014) The potent cytotoxicity of reactive oxygen species (ROS) can cause various diseases but may also serve as a powerful weapon capable of destroying cancer cells. Although the balance between generation ... |
| 3-Carboxy-4-nitrophenyl disulfide |
| EINECS 200-714-4 |
| 3,3'-Disulfanediylbis(6-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| Benzoic acid, 3,3'-dithiobis[6-nitro- |
| Ellman Reagent |
| MFCD00007140 |
| 5,5'-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| 5,5'-DITHIOBIS(2-NITROBENZOIC ACID) |
| 5,5'-Dithobis(2-Nitrobenzoic Acid) |
| 5,5-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| 5,5′-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| UNII:9BZQ3U62JX |
| DTNB |
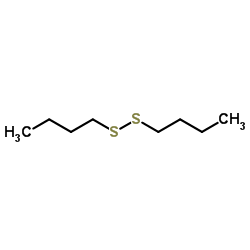 CAS#:629-45-8
CAS#:629-45-8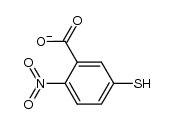 CAS#:18430-02-9
CAS#:18430-02-9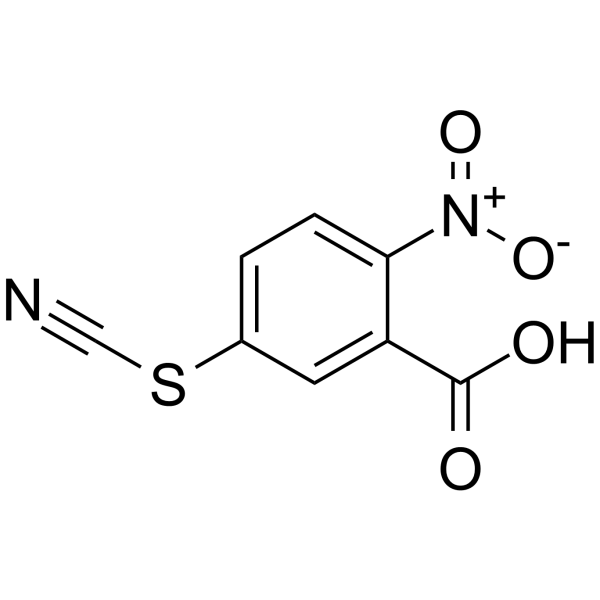 CAS#:30211-77-9
CAS#:30211-77-9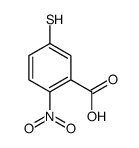 CAS#:15139-21-6
CAS#:15139-21-6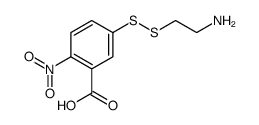 CAS#:71899-86-0
CAS#:71899-86-0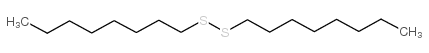 CAS#:822-27-5
CAS#:822-27-5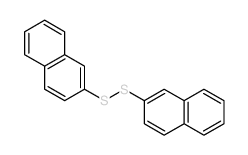 CAS#:5586-15-2
CAS#:5586-15-2
