Pentachloropseudilin
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 11:30:46
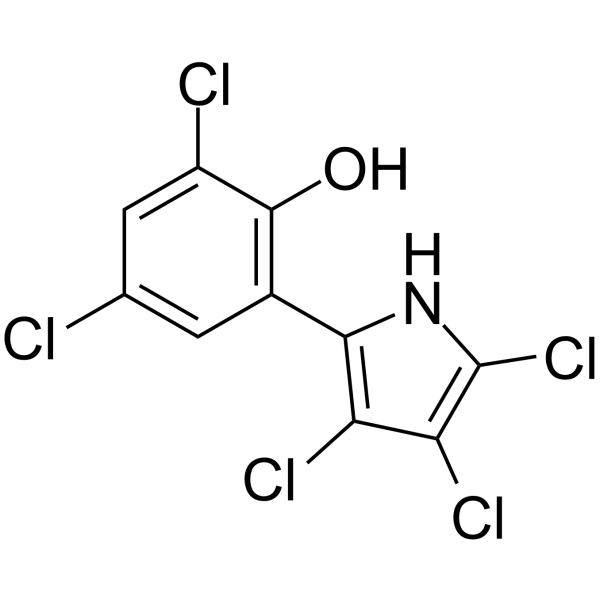
Pentachloropseudilin structure
|
Common Name | Pentachloropseudilin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 69640-38-6 | Molecular Weight | 331.41 | |
| Density | 1.733g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 445.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H4Cl5NO | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 223.5ºC | |
Use of PentachloropseudilinPentachloropseudilin (Antibiotic A 15104 Y; PClP) is a reversible and allosteric potent inhibitor of Myo1s (class 1 myosins) with IC50s range from 1 to 5 μM for mammalian class-1 myosins and greater than 90 μM for class-2 and class-5 myosins. Pentachloropseudilin is a potent inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-stimulated signaling, with an IC50 of 0.1 to 0.2 μM for TGF-β[1][2]. |
| Name | 2,4-Dichloro-6-(3,4,5-trichloro-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)phenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pentachloropseudilin (Antibiotic A 15104 Y; PClP) is a reversible and allosteric potent inhibitor of Myo1s (class 1 myosins) with IC50s range from 1 to 5 μM for mammalian class-1 myosins and greater than 90 μM for class-2 and class-5 myosins. Pentachloropseudilin is a potent inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-stimulated signaling, with an IC50 of 0.1 to 0.2 μM for TGF-β[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Pentachloropseudilin (PClP) inhibits TGF-β-stimulated Smad2/3 phosphorylation and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) promoter activation with an IC50 of 0.1 μM in target cells (A549, HepG2, and Mv1Lu cells)[1]. Pentachloropseudilin attenuates TGF-β-stimulated expression of vimentin, N-cadherin, and fibronectin and, thus, blocks TGF-β-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in these cells. Pentachloropseudilin (0.05 to 1 μΜ; 0-6 hours) pretreatment inhibits TGF-β-mediated (50 or 100 pM) increases in p-Smad2/3 expression to 47% (Mv1Lu) and 79% (A549), respectively[1]. Pentachloropseudilin (0.2 μM) suppresses TGF-β-stimulated cellular responses by attenuating cell-surface expression of the type II TGF-β receptor through accelerating caveolae-mediated internalization followed by primarily lysosome-dependent degradation of the receptor, as demonstrated by sucrose density gradient analysis and immune fluorescence staining[1]. Pentachloropseudilin (200 μM; 24 hours) exhibits and altered cell viability in HUVECs[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.733g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 445.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C10H4Cl5NO |
| Molecular Weight | 331.41 |
| Flash Point | 223.5ºC |
| Exact Mass | 328.87400 |
| PSA | 36.02000 |
| LogP | 5.65430 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.672 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|
|
~79% 
Pentachloropseudilin CAS#:69640-38-6 |
| Literature: Martin, Rene; Jaeger, Anne; Bohl, Markus; Richter, Sabine; Fedorov, Roman; Manstein, Dietmar J.; Gutzeit, Herwig O.; Knolker, Hans-Joachim Angewandte Chemie - International Edition, 2009 , vol. 48, # 43 p. 8042 - 8046 |
|
~% 
Pentachloropseudilin CAS#:69640-38-6 |
| Literature: KINARIS BIOMEDICALS GMBH Patent: US2011/105554 A1, 2011 ; |
| 2xel |
| Pentachloropseudilin |