9-Anthracenecarboxylic acid

9-Anthracenecarboxylic acid structure
|
Common Name | 9-Anthracenecarboxylic acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 723-62-6 | Molecular Weight | 222.239 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 467.5±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O2 | Melting Point | 213-217 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 206.1±14.8 °C | |
Use of 9-Anthracenecarboxylic acidAnthracene-9-carboxylic acid (9-Anthracenecarboxylic acid) is an anthracene derivative traditionally used to block and identify Ca2+-activated Cl- currents (CaCCs) in various cell types, like diverse smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells and salivary gland cells[1]. |
| Name | 9-anthroic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid (9-Anthracenecarboxylic acid) is an anthracene derivative traditionally used to block and identify Ca2+-activated Cl- currents (CaCCs) in various cell types, like diverse smooth muscle cells, epithelial cells and salivary gland cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Ca2+-activated Cl- currents[1] |
| In Vitro | Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid causes a voltage-dependent block of outward currents in HEK 293T cells and inhibits a larger fraction of the current as depolarization increased[1]. Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid induces a strong potentiation of tail currents measured at -100 mV after depolarizing voltages, as well as a prolongation of the deactivation kinetics in HEK 293T[1]. Anthracene-9-carboxylic acid (500 μM, rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells) produces a small inhibition of the maximum outward Cl- current at +70 mV (21±10%) but augmented the amplitude of the instantaneous inward relaxation at -80 mV by 321±34%[2]. |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 467.5±14.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 213-217 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 222.239 |
| Flash Point | 206.1±14.8 °C |
| Exact Mass | 222.068085 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 4.36 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.743 |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | CB8764000 |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2916399090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2916399090 other aromatic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides, peroxyacids and their derivatives VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Role of anoctamin-1 and bestrophin-1 in spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain in rats.
Mol. Pain 11 , 41, (2015) Calcium-activated chloride channels (CaCCs) activation induces membrane depolarization by increasing chloride efflux in primary sensory neurons that can facilitate action potential generation. Previou... |
|
|
Integrated microfluidic chip and online SCX separation allows untargeted nanoscale metabolomic and peptidomic profiling.
J. Proteome Res. 14(3) , 1621-6, (2015) Metabolomics and peptidomics are systems biology approaches in which broad populations of molecular species produced in a cell or tissue sample are identified and quantified. These two molecular popul... |
|
|
Extracellular magnesium and calcium reduce myotonia in isolated ClC-1 chloride channel-inhibited human muscle.
Muscle Nerve 51(1) , 65-71, (2015) Experimental myotonia induced in rat muscle by ClC-1 chloride channel-inhibited has been shown to be related inversely to extracellular concentrations of Mg(2+) and Ca(2+) ([Mg(2+) ]o and [Ca(2+) ]o) ... |
| 9-Anthroic acid |
| EINECS 211-964-9 |
| 9-Carboxyanthracene |
| ANCA |
| anthracene-9-carboxylic acid |
| MFCD00001257 |
| 9-Anthracene carboxylic acid |
| anthracenecarboxylic acid |
| 9-Anthracenecarboxylic acid |
| Polyoxyethylenesorbitan monolaurate |
 CAS#:124-38-9
CAS#:124-38-9 CAS#:120-12-7
CAS#:120-12-7 CAS#:22362-86-3
CAS#:22362-86-3 CAS#:642-31-9
CAS#:642-31-9 CAS#:1564-64-3
CAS#:1564-64-3 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2 CAS#:79-37-8
CAS#:79-37-8 CAS#:141-82-2
CAS#:141-82-2 CAS#:40476-29-7
CAS#:40476-29-7 CAS#:20202-05-5
CAS#:20202-05-5 CAS#:613-31-0
CAS#:613-31-0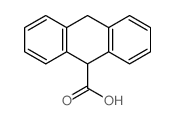 CAS#:1143-20-0
CAS#:1143-20-0 CAS#:84-65-1
CAS#:84-65-1 CAS#:779-03-3
CAS#:779-03-3 CAS#:523-27-3
CAS#:523-27-3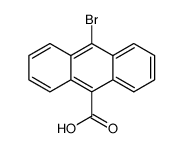 CAS#:6929-81-3
CAS#:6929-81-3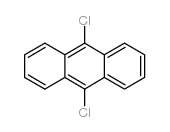 CAS#:605-48-1
CAS#:605-48-1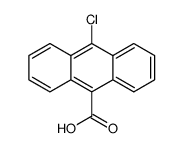 CAS#:6929-82-4
CAS#:6929-82-4
