ACES
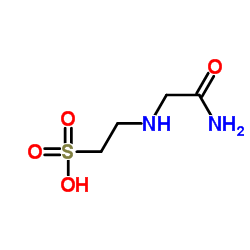
ACES structure
|
Common Name | ACES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7365-82-4 | Molecular Weight | 182.198 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10N2O4S | Melting Point | >220 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of ACESACES (N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is a zwitterionic buffer. The working pH range of ACES buffer is 6.8-7.2[1][2]. |
| Name | N-(2-acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | ACES (N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is a zwitterionic buffer. The working pH range of ACES buffer is 6.8-7.2[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | >220 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10N2O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 182.198 |
| Exact Mass | 182.036133 |
| PSA | 117.87000 |
| LogP | -3.24 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.537 |
| InChIKey | DBXNUXBLKRLWFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | NC(=O)CNCCS(=O)(=O)O |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29241900 |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Xanthine derivatives quantification in serum by capillary zone electrophoresis.
J. Chromatogr. Sci. 52(9) , 1121-6, (2014) A capillary electrophoresis method was developed to quantify caffeine and theophylline, xanthine derivatives with bronchodilator activity. Buffer concentration, pH and applied voltage were optimized u... |
|
|
Characterization of asparagine 330 deamidation in an Fc-fragment of IgG1 using cation exchange chromatography and peptide mapping.
J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 965 , 65-71, (2014) Deamidation is one of the most common degradation pathways for proteins and frequently occurs at "hot spots" with Asn-Gly, Asn-Ser or Asn-Thr sequences. Occasionally, deamidation may occur at other mo... |
|
|
Phosphate modulates receptor sulfotyrosine recognition by the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2).
Org. Biomol. Chem. 13(7) , 2162-9, (2015) Tyrosine sulfation is a widespread post-translational modification that mediates the interactions of secreted and membrane-associated proteins in such varied biological processes as peptide hormone ac... |
| 2-[(carbamoylmethyl)amino]ethanesulfonic acid |
| Ethanesulfonic acid, 2-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]- |
| 2-[(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]ethanesulfonic acid |
| EINECS 230-908-4 |
| N-(Carbamoylmethyl)taurine |
| N-(2-Acetamido)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid |
| N-(Carbamoylmethyl)-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid |
| MFCD00008030 |
| Ethanesulfonic acid, {2-[(2-amino-2-oxoethyl)amino]-} |
| ACES |

