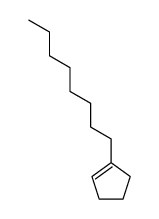
δ-Tridecalactone

δ-Tridecalactone structure
|
Common Name | δ-Tridecalactone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 7370-92-5 | Molecular Weight | 212.329 | |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 309.1±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H24O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese | Flash Point | 126.5±16.4 °C | |
| Name | δ-Tridecanolactone |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 309.1±10.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H24O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 212.329 |
| Flash Point | 126.5±16.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 212.177628 |
| PSA | 26.30000 |
| LogP | 4.01 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.450 |
| InChIKey | RZZLMGATMUAJPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCC1CCCC(=O)O1 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|
~99% 
δ-Tridecalactone CAS#:7370-92-5 |
| Literature: Hsu; Fang Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2001 , vol. 66, # 25 p. 8573 - 8584 |
|
~% 
δ-Tridecalactone CAS#:7370-92-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 66, # 25 p. 8573 - 8584 |
|
~% 
δ-Tridecalactone CAS#:7370-92-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 66, # 25 p. 8573 - 8584 |
|
~% 
δ-Tridecalactone CAS#:7370-92-5 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 66, # 25 p. 8573 - 8584 |
|
~78% 
δ-Tridecalactone CAS#:7370-92-5 |
| Literature: Abbasov; Alimardanov; Suleimanova Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry, 1997 , vol. 70, # 4 p. 621 - 626 |
| HS Code | 2932999099 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2932999099. other heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Preparation of Optically Active δ-Tri- and δ-Tetradecalactones by a Combination of Novozym 435-catalyzed Enantioselective Methanolysis and Amidation.
J. Oleo Sci. 64(11) , 1213-26, (2015) A combination of Novozym 435-catalyzed methanolysis and amidation using racemic N-methyl-5-acetoxytridecan- and tetradecanamides as a substrate proceeded in good enantioselectivity to afford the corre... |
|
|
Two distinct pathways for the formation of hydroxy FA from linoleic acid by lactic acid bacteria.
Lipids 38(12) , 1269-74, (2003) Twenty-three of 86 strains of lactic acid bacteria transformed linoleic acid into hydroxy FA. Two distinct conversion pathways were in operation. Two strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus and a strain ... |
| 2H-Pyran-2-one,tetrahydro-6-octyl |
| 6-Octyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one |
| 5-tridecanolide |
| 5-Hydroxytridecanoic acid lactone |
| delta-Tridecanolactone |
| TRIDECANO-1,5-LACTONE |
| δ-Tridecanolactone |
| tetrahydro-6-octyl-2h-pyran-2-on |
| δ-Tridecalactone |
| 2H-Pyran-2-one, tetrahydro-6-octyl- |
| 6-octyl-tetrahydro-pyran-2-one |
| Tetrahydro-6-octyl-2H-pyran-2-one |
| tridecanolactone |