isobutanol
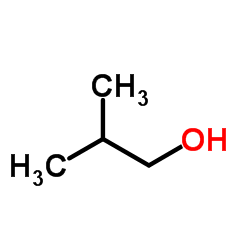
isobutanol structure
|
Common Name | isobutanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 78-83-1 | Molecular Weight | 74.122 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 105.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10O | Melting Point | −108 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 27.8±0.0 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | isobutanol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 105.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | −108 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10O |
| Molecular Weight | 74.122 |
| Flash Point | 27.8±0.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 74.073166 |
| PSA | 20.23000 |
| LogP | 0.69 |
| Vapour density | 2.55 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 16.4±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.393 |
| InChIKey | ZXEKIIBDNHEJCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(C)CO |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, aluminium. |
| Water Solubility | 95 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H226-H315-H318-H335-H336 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P280-P304 + P340 + P312-P305 + P351 + P338 + P310-P403 + P235 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant |
| Risk Phrases | R10;R37/38;R41;R67 |
| Safety Phrases | S13-S26-S37/39-S46-S7/9 |
| RIDADR | UN 1212 3/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | NP9625000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 3 |
| HS Code | 2905141000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2905141000 |
|---|
|
Combined effects of nutrients and temperature on the production of fermentative aromas by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during wine fermentation.
Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99(5) , 2291-304, (2015) Volatile compounds produced by yeast during fermentation greatly influence the organoleptic qualities of wine. We developed a model to predict the combined effects of initial nitrogen and phytosterol ... |
|
|
The exometabolome of Clostridium thermocellum reveals overflow metabolism at high cellulose loading.
Biotechnol. Biofuels 7(1) , 155, (2014) Clostridium thermocellum is a model thermophilic organism for the production of biofuels from lignocellulosic substrates. The majority of publications studying the physiology of this organism use subs... |
|
|
Convenient QSAR model for predicting the complexation of structurally diverse compounds with β-cyclodextrins
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 17 , 896-904, (2009) This paper reports a QSAR study for predicting the complexation of a large and heterogeneous variety of substances (233 organic compounds) with beta-cyclodextrins (beta-CDs). Several different theoret... |
| i-Butyl alcohol |
| Methylethyl carbinol |
| iso-butanol |
| 1-Propanol, 2-methyl- |
| 2-methyl propyl alcohol |
| isobutyl alcohol |
| Propanol, 2-methyl- |
| 1-hydroxymethylpropane |
| 2-methyl-1-propanyl alcohol |
| 2-Methyl-1-propanol |
| 2-Methylpropan-1-ol |
| iso-Butyl Alcohol |
| 2-Methylpropyl alcohol |
| 2-Methyl propanol |
| UNII-56F9Z98TEM |
| 2-MethylpropanoI |
| isopropylcarbinol |
| EINECS 201-148-0 |
| i-Butanol |
| 2-methylpropanol |
| isobutanol |
| MFCD00004740 |
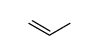 CAS#:187737-37-7
CAS#:187737-37-7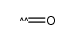 CAS#:201230-82-2
CAS#:201230-82-2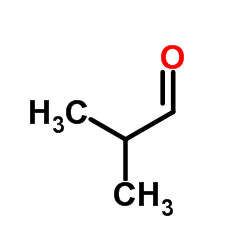 CAS#:78-84-2
CAS#:78-84-2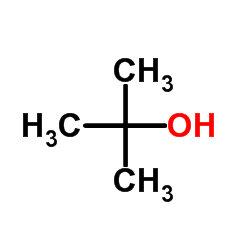 CAS#:75-65-0
CAS#:75-65-0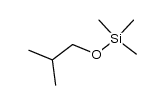 CAS#:18269-50-6
CAS#:18269-50-6 CAS#:2516-33-8
CAS#:2516-33-8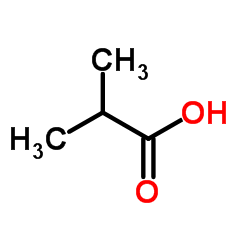 CAS#:79-31-2
CAS#:79-31-2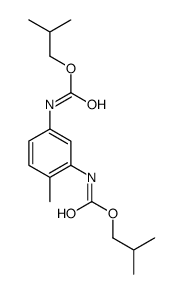 CAS#:71412-40-3
CAS#:71412-40-3 CAS#:50-00-0
CAS#:50-00-0 CAS#:1221-65-4
CAS#:1221-65-4 CAS#:1081-32-9
CAS#:1081-32-9 CAS#:17085-91-5
CAS#:17085-91-5 CAS#:10565-10-3
CAS#:10565-10-3 CAS#:2876-35-9
CAS#:2876-35-9![2-isopropyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/196/5851-43-4.png) CAS#:5851-43-4
CAS#:5851-43-4 CAS#:3972-56-3
CAS#:3972-56-3 CAS#:542-55-2
CAS#:542-55-2 CAS#:67-64-1
CAS#:67-64-1 CAS#:547-63-7
CAS#:547-63-7
