Spiramycin
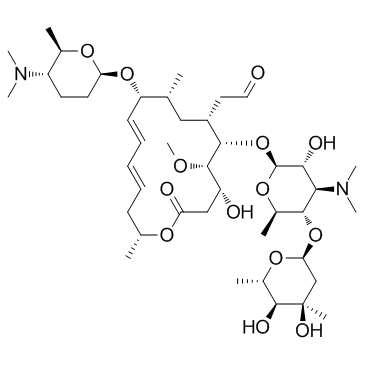
Spiramycin structure
|
Common Name | Spiramycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 8025-81-8 | Molecular Weight | 843.053 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 913.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C43H74N2O14 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 506.4±34.3 °C | |
Use of SpiramycinSpiramycin is a clinically important 16-member macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens. |
| Name | Spiramycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Spiramycin is a clinically important 16-member macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Bacterial[1] |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 913.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C43H74N2O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 843.053 |
| Flash Point | 506.4±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 842.513977 |
| LogP | 3.06 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.550 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | 36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-36-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | WG9400000 |
| HS Code | 29419090 |
|
Regulation of the biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic spiramycin in Streptomyces ambofaciens.
J. Bacteriol. 192(21) , 5813-21, (2010) Streptomyces ambofaciens synthesizes the macrolide antibiotic spiramycin. The biosynthetic gene cluster for spiramycin has been characterized for S. ambofaciens. In addition to the regulatory gene srm... |
|
|
A spicamycin derivative (KRN5500) provides neuropathic pain relief in patients with advanced cancer: a placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept trial.
J. Pain Symptom Manage. 43(4) , 679-93, (2012) Neuropathic pain in patients with cancer can be difficult to treat effectively.The purpose of the study was to determine safety and efficacy of KRN5500, a novel, spicamycin-derived, nonopioid analgesi... |
|
|
Influences of two antibiotic contaminants on the production, release and toxicity of microcystins
Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 77 , 79-87, (2012) The influences of spiramycin and amoxicillin on the algal growth, production and release of target microcystins (MCs), MC-LR, MC-RR and MC-YR, in Microcystis aeruginosa were investigated through the s... |
| [(4R,5S,6S,7R,9R,10R,11E,13E,16R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4R,5S,6S)-4,5-Dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-10-{[(2R,5S,6S)-5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxooxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-7-yl]acetaldehyde (non-preferred name) |
| Leucomycin |
| Foromacidin |
| Provamycin |
| [(4R,5S,6S,7R,9R,10R,11E,13E,16R)-6-{[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4R,5S,6S)-4,5-Dihydroxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-10-{[(2R,5S,6S)-5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxooxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-7-yl]acetaldehyde |
| Spiramycin I |
| Rovamycin |

