Hylambatin
Modify Date: 2024-01-08 17:23:09
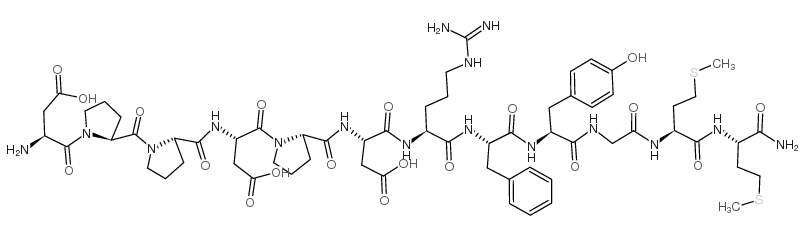
Hylambatin structure
|
Common Name | Hylambatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 80890-46-6 | Molecular Weight | 1439.61000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C63H90N16O19S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of HylambatinHylambatin, a tachykinin, increases both plasma glucose and plasma insulin, whereas the secretion of glucagon was not affected. Hylambatin can be used in diabetes research[1]. |
| Name | hylambatin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hylambatin, a tachykinin, increases both plasma glucose and plasma insulin, whereas the secretion of glucagon was not affected. Hylambatin can be used in diabetes research[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C63H90N16O19S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1439.61000 |
| Exact Mass | 1438.60000 |
| PSA | 607.47000 |
| LogP | 1.19880 |
|
~% 
Hylambatin CAS#:80890-46-6 |
| Literature: Okamoto, Kenji; Yasumura, Koichi; Fujitani, Kazuyoshi; Katakura, Shinichi; Akaji, Kenichi; et al. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 2 p. 430 - 437 |
|
~% 
Hylambatin CAS#:80890-46-6 |
| Literature: Okamoto, Kenji; Yasumura, Koichi; Fujitani, Kazuyoshi; Katakura, Shinichi; Akaji, Kenichi; et al. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1984 , vol. 32, # 2 p. 430 - 437 |
| H-ASP-PRO-PRO-ASP-PRO-ASP-ARG-PHE-TYR-GLY-MET-MET-NH2 |
| L-Asp-L-Pro-L-Pro-L-Asp-L-Pro-L-Asp-L-Arg-L-Phe-L-Tyr-Gly-L-Met-L-Met-NH2 |
| H-Asp-Pro-Pro-Asp-Pro-Asp-Arg-Phe-Tyr-Gly-Met-Met-NH2 (hylambatin) |
| ASP-PRO-PRO-ASP-PRO-ASP-ARG-PHE-TYR-GLY-MET-NH2 |
| ASP-PRO-PRO-ASP-PRO-ASP-ARG-PHE-TYR-GLY-MET-MET-NH2 |



