Cyclosomatostatin
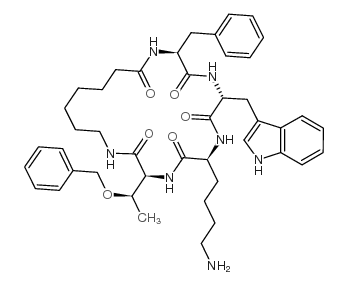
Cyclosomatostatin structure
|
Common Name | Cyclosomatostatin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 84211-54-1 | Molecular Weight | 779.96700 | |
| Density | 1.147g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 1118.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C44H57N7O6 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 630.2ºC | |
Use of CyclosomatostatinCyclosomatostatin is a potent somatostatin (SST) receptor antagonist. Cyclosomatostatin can inhibit somatostatin receptor type 1 (SSTR1) signaling and decreases cell proliferation, ALDH+ cell population size and sphere-formation in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells[1]. |
| Name | Somatostatin Antagonist |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cyclosomatostatin is a potent somatostatin (SST) receptor antagonist. Cyclosomatostatin can inhibit somatostatin receptor type 1 (SSTR1) signaling and decreases cell proliferation, ALDH+ cell population size and sphere-formation in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.147g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1118.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C44H57N7O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 779.96700 |
| Flash Point | 630.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 779.43700 |
| PSA | 196.54000 |
| LogP | 6.05120 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.558 |
| InChIKey | YHVHQZYJGWGAKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CC(OCc1ccccc1)C1NC(=O)C(CCCCN)NC(=O)C(Cc2c[nH]c3ccccc23)NC(=O)C(Cc2ccccc2)NC(=O)CCCCCCNC1=O |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Frequency-dependent, cell type-divergent signaling in the hippocamposeptal projection.
J. Neurosci. 34(35) , 11769-80, (2014) Hippocampal oscillations are critical for information processing, and are strongly influenced by inputs from the medial septum. Hippocamposeptal neurons provide direct inhibitory feedback from the hip... |
|
|
Effects of somatostatin on the responses of rostrally projecting spinal dorsal horn neurons to noxious stimuli in cats.
Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 12(5) , 253-8, (2008) Somatostatin (SOM) is a widely distributed peptide in the central nervous system and exerts a variety of hormonal and neural actions. Although SOM is assumed to play an important role in spinal nocice... |
|
|
Oral curcumin has anti-arthritic efficacy through somatostatin generation via cAMP/PKA and Ca(2+)/CaMKII signaling pathways in the small intestine.
Pharmacol. Res. 95-96 , 71-81, (2015) Curcumin (CUR) has been proven to be clinically effective in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy, but its low oral bioavailability eclipses existent evidence that attempts to explain the underlying mech... |
| Cyclosomatostatin |
| C[AMINOHEPTANOYL-PHE-DTRP-LYS-THR: BZL] |
| 6-(4-aminobutyl)-12-benzyl-9-(1H-indol-3-ylmethyl)-3-(1-phenylmethoxyethyl)-1,4,7,10,13-pentazacycloicosane-2,5,8,11,14-pentone |
| Cyclo(7-Aminoheptanoyl-Phe-D-Trp-Lys-Thr[Bzl]) |