Hexaflumuron
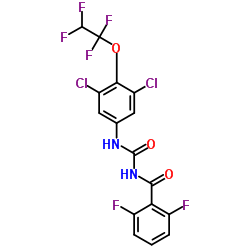
Hexaflumuron structure
|
Common Name | Hexaflumuron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 86479-06-3 | Molecular Weight | 461.143 | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H8Cl2F6N2O3 | Melting Point | 202-205ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of HexaflumuronHexazinone is a nonselective herbicide from the triazine family. Hexazinone binds to the D-1 quinone protein of the electron transport chain in photosystem II to inhibit the photosynthesis[1]. |
| Name | Hexaflumuron |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Hexazinone is a nonselective herbicide from the triazine family. Hexazinone binds to the D-1 quinone protein of the electron transport chain in photosystem II to inhibit the photosynthesis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 202-205ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C16H8Cl2F6N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 461.143 |
| Exact Mass | 459.981628 |
| PSA | 67.43000 |
| LogP | 5.87 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.548 |
| InChIKey | RGNPBRKPHBKNKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(NC(=O)c1c(F)cccc1F)Nc1cc(Cl)c(OC(F)(F)C(F)F)c(Cl)c1 |
| Storage condition | 0-6°C |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H332-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S60-S61 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 |
| RTECS | CV3800000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
|
Comparison of two ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction approaches for the determination of benzoylurea insecticides in wastewater using liquid chromatography-quadrupole-linear ion trap-mass spectrometry: evaluation of green parameters.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1356 , 1-9, (2014) Two dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (DLLME) approaches including temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction (TCIL-DLLME) and ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid... |
|
|
Mark-recapture without estimating population sizes: a tool to evaluate termite baits.
Bull. Entomol. Res. 96(2) , 99-103, (2006) The mark-recapture technique is currently being used by many termite researchers. Here its two uses are explained and disentangled. Use 1 is mapping the geographical location of the colony and use 2 i... |
|
|
Disruption of reproductive activity of Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) primary reproductives by three chitin synthesis inhibitors.
J. Econ. Entomol. 97(6) , 2015-20, (2004) Effects of the chitin synthesis inhibitors (CSIs) diflubenzuron, hexaflumuron, and lufenuron on the Formosan subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki, primary reproductives were studied in... |
| Hexafluron |
| Hexaflumuron |
| N-{[3,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)phenyl]carbamoyl}-2,6-difluorobenzamide |
| OMS-3031 |
| N-[[[3,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide |
| CONSULT |
| DE-473 |
| MFCD01743935 |
| 1-[3,5-dichloro-4-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethoxy)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea |
| Trueno |
| xrd473 |
| CONSOL |
| hexafluoron |

