Vonoprazan
Modify Date: 2025-12-08 11:10:42
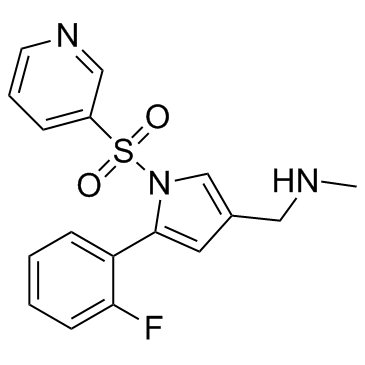
Vonoprazan structure
|
Common Name | Vonoprazan | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 881681-00-1 | Molecular Weight | 345.391 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 530.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H16FN3O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 274.5±32.9 °C | |
Use of VonoprazanTAK-438 (free base) is a novel P-CAB (potassium-competitive acid blocker) that reversibly inhibits H+/K+ ATPase with IC50 of 19 nM (pH 6.5), controls gastric acid secretion.IC50 value: 19 nM [1]Target: H+/K+ ATPasein vitro: TAK-438 is a pyrrole derivative with a chemical structure that is completely different from the P-CABs developed to date. TAK-438 inhibits gastric H+/K+ ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner. Under neutral conditions (pH 7.5), the inhibitory activity of TAK-438 is almost the same as that under weakly acidic conditions (pH 6.5). TAK-438 does not inhibit Na+/K+ ATPase activity even at concentration 500 times higher than their IC50 values against gastric H+/K+ ATPase activity. TAK-438 inhibits gastric H+/K+ ATPase in a K+ competitive manner with Ki of 3 nM [2]. in vivo: TAK-438 inhibits basal gastric acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner, and the ID50 value is 1.26 mg/kg. Intravenous administration of TAK-438 dose-dependently increases the pH of the gastric perfusate, and the increase in pH is sustained for 5 h after administration. At the 1 mg/kg dose, the pH plateaues 90 min after administration, and the highest pH value reached is 5.9 [2]. In addition, TAK-438 shows a potent and longer-lasting inhibitory effect on the histamine-stimulated gastric acid secretion in rats and dogs. TAK-438 shows significant antisecretory activity through high accumulation and slow clearance from the gastric tissue. TAK-438 is unaffected by the gastric secretory state, unlike PPIs [3]. |
| Name | Vonoprazan |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | TAK-438 (free base) is a novel P-CAB (potassium-competitive acid blocker) that reversibly inhibits H+/K+ ATPase with IC50 of 19 nM (pH 6.5), controls gastric acid secretion.IC50 value: 19 nM [1]Target: H+/K+ ATPasein vitro: TAK-438 is a pyrrole derivative with a chemical structure that is completely different from the P-CABs developed to date. TAK-438 inhibits gastric H+/K+ ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner. Under neutral conditions (pH 7.5), the inhibitory activity of TAK-438 is almost the same as that under weakly acidic conditions (pH 6.5). TAK-438 does not inhibit Na+/K+ ATPase activity even at concentration 500 times higher than their IC50 values against gastric H+/K+ ATPase activity. TAK-438 inhibits gastric H+/K+ ATPase in a K+ competitive manner with Ki of 3 nM [2]. in vivo: TAK-438 inhibits basal gastric acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner, and the ID50 value is 1.26 mg/kg. Intravenous administration of TAK-438 dose-dependently increases the pH of the gastric perfusate, and the increase in pH is sustained for 5 h after administration. At the 1 mg/kg dose, the pH plateaues 90 min after administration, and the highest pH value reached is 5.9 [2]. In addition, TAK-438 shows a potent and longer-lasting inhibitory effect on the histamine-stimulated gastric acid secretion in rats and dogs. TAK-438 shows significant antisecretory activity through high accumulation and slow clearance from the gastric tissue. TAK-438 is unaffected by the gastric secretory state, unlike PPIs [3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 530.3±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C17H16FN3O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 345.391 |
| Flash Point | 274.5±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 345.094727 |
| LogP | 2.74 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.622 |
| InChIKey | BFDBKMOZYNOTPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CNCc1cc(-c2ccccc2F)n(S(=O)(=O)c2cccnc2)c1 |
| 1H-Pyrrole-3-methanamine, 5-(2-fluorophenyl)-N-methyl-1-(3-pyridinylsulfonyl)- |
| Vonoprazan |
| 1-[5-(2-Fluorophenyl)-1-(3-pyridinylsulfonyl)-1H-pyrrol-3-yl]-N-methylmethanamine |
| TAK-438 |

