Aspartate aminotransferase
Aspartate aminotransferase structure
|
Common Name | Aspartate aminotransferase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 9000-97-9 | Molecular Weight | 477.550 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
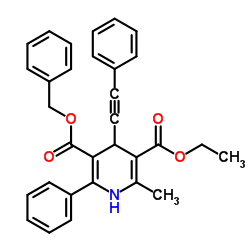
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C | |
Use of Aspartate aminotransferaseAspartate aminotransferase (AST) is a transaminase enzyme, is often used in biochemical studies. Aspartate aminotransferase catalyzes aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate converts to oxaloacetate and glutamate. Aspartate aminotransferase can be found in cerebrospinal fluid, exudates, and transudates[1]. |
| Name | Aminotransferase aspartate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is a transaminase enzyme, is often used in biochemical studies. Aspartate aminotransferase catalyzes aspartate and alpha-ketoglutarate converts to oxaloacetate and glutamate. Aspartate aminotransferase can be found in cerebrospinal fluid, exudates, and transudates[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 643.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C31H27NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 477.550 |
| Flash Point | 342.7±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 477.194000 |
| LogP | 7.16 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | S22;S24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
The effectiveness of fermented turmeric powder in subjects with elevated alanine transaminase levels: a randomised controlled study.
BMC Complement Altern. Med. 13 , 58, (2013) Previous animal studies have shown that Curcuma longa (turmeric) improves liver function. Turmeric may thus be a promising ingredient in functional foods aimed at improving liver function. The purpose... |
|
|
Does liver damage explain the inverse association between vitamin D status and mortality?
Ann. Epidemiol. 23(12) , 812-4, (2013) Several observational studies have linked vitamin D deficiency with an increased risk of all cause mortality. Vitamin D deficiency is common among patients with liver diseases. In a random sample of t... |
|
|
Plasma level of atherogenic and anti-atherogenic factors among palm wine drinkers of rural southwest Nigeria.
Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 41(4) , 337-47, (2012) Scientific evidence indicates that light to moderate drinking on a daily basis may significantly reduce the risks of coronary heart disease (CHD). In contrast, excessive alcohol intake and binge drink... |
| MFCD00131191 |
| AST |
| Aspartate-2-oxoglutarate transaminase |
| Aspartic acid aminotransferase |
| EINECS 232-571-9 |
| 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |
| 2-Oxoglutarate-glutamate aminotransferase |
| Aspartate aminotransferase |
| Aspartic aminotransferase |
| 3,5-Pyridinedicarboxylic acid, 1,4-dihydro-2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(2-phenylethynyl)-, 3-ethyl 5-(phenylmethyl) ester |
| Aspartate alpha-ketoglutarate transaminase |
| 5-Benzyl 3-ethyl 2-methyl-6-phenyl-4-(phenylethynyl)-1,4-dihydro-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate |