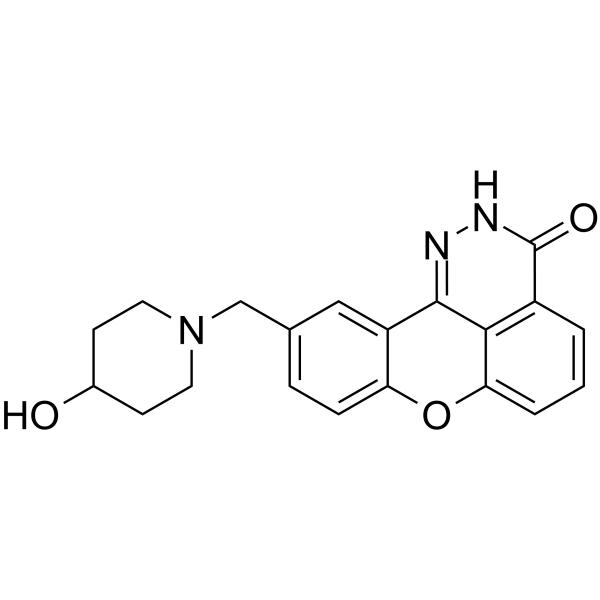
| Description |
E7016 (GPI 21016) is an orally available PARP inhibitor. E7016 can enhance tumor cell radiosensitivity in vitro and in vivo through the inhibition of DNA repair. E7016 acts as a potential anticancer agent[1][2].
|
| Related Catalog |
|
| Target |
PARP
|
| In Vitro |
E7016 can enhance tumor cell radiosensitivity through the inhibition of DNA repair[1]. E7016 (3 μM)-mediated radiosensitization occurs through an increase in the number of cells undergoing mitotic catastrophe and not an increase in the number of cells undergoing apoptosis[1]. E7016 inhibits PARP by mimicking NAD+[2]. Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Line: The U251 human glioblastoma cell line Concentration: 3 μM Incubation Time: 6 hours prior to irradiation and were stained at 24 and 72 h postirradiation Result: The number of cells in mitotic catastrophe was significantly greater in the E7016-treated irradiated cells than in cells that received radiation only at 24 hours postirradiation.
|
| In Vivo |
E7016 has antitumor efficacy in murine xenograft studies[1]. Administration of E7016 (40 mg/kg; oral gavage) to mice bearing U251 xenografts enhances the effectiveness of the Temozolomide/radiation combination[1]. Mice treated with E7016/irradiation/Temozolomide have an additional growth delay of six days compared with the combination of Temozolomide and irradiation in vivo[1]. Animal Model: Four- to six-week-old female nude mice[3] Dosage: 40 mg/kg Administration: Oral gavage Result: E7016 enhanced the radiation/Temozolomide (3 mg/kg orally)-induced tumor growth delay of U251 xenografts.
|
| References |
[1]. Andrea L Russo, et al. In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization of glioblastoma cells by the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor E7016. Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Jan 15;15(2):607-12. [2]. W George Lai, et al. A Baeyer-Villiger oxidation specifically catalyzed by human flavin-containing monooxygenase 5. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Jan;39(1):61-70.
|