γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine
Modify Date: 2024-01-12 09:27:14
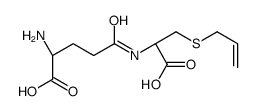
γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine structure
|
Common Name | γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 91216-95-4 | Molecular Weight | 290.33600 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C11H18N2O5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteineγ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (L-γ-Glutamyl-(S)-Allyl-Cysteine) is a naturally occurring organosulfur compound found in garlic. γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine has antiglycative effect and shows radical-scavenging and metal-chelating capacities[1][2]. |
| Name | (2S)-2-amino-5-[[(1R)-1-carboxy-2-prop-2-enylsulfanylethyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (L-γ-Glutamyl-(S)-Allyl-Cysteine) is a naturally occurring organosulfur compound found in garlic. γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine has antiglycative effect and shows radical-scavenging and metal-chelating capacities[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (L-γ-Glutamyl-(S)-Allyl-Cysteine; 0.1-2.5 mg/mL) inhibits the increase of fluorescence intensity at about 440 nm in a concentration-dependent manner and reduces reacted free lysine side chains[1]. γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (2.5 mg/mL) prevents Glycation-specific decline in BSA α-helix content and increase in β-sheet in vitro[1]. γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (2.5 mg/mL) suppresses protein crosslinking to form polymers[1]. γ-Glutamyl-S-allylcysteine (10, 40, 160 μg/mL) shows radical-scavenging and metal-chelating capacities[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C11H18N2O5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 290.33600 |
| Exact Mass | 290.09400 |
| PSA | 158.51000 |
| LogP | 1.20770 |
| unii-1o5qgm20nb |