Pyronin Y
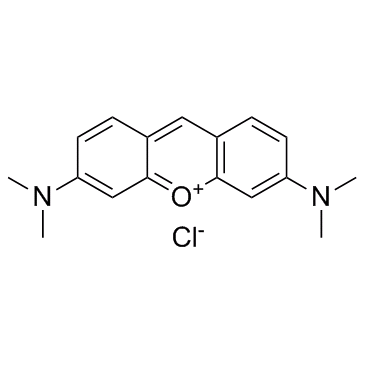
Pyronin Y structure
|
Common Name | Pyronin Y | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 92-32-0 | Molecular Weight | 302.799 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H19ClN2O | Melting Point | 250-260ºC(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Pyronin YPyronin Y is an intercalating cationic dye that shows specificity towards RNA. |
| Name | acridine red 3B |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Pyronin Y is an intercalating cationic dye that shows specificity towards RNA. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Pyronin Y forms fluorescent complexes with double-stranded nucleic acids, especially RNA, enabling semi-quantitative analysis of cellular RNA in flow cytometry, to estimate the RNA content per cell in formalin fixed EL4 leukosis tumor cells, enzyme dispersed R3327-G rat prostatic adenocarcinoma cells, mouse spleen cells stimulated with concanavalin A, and human peripheral blood lymphocytes stimulated with phytohemagglutinin[1]. A fluorescent staining procedure based on pyronin Y is described. The technique has been used to stain RNA in human reticulocytes for subsequent flow analysis and sorting[2]. In viable cells this dye also accumulates in mitochondria. At a concentration of 1.7 to 3.3 μM, pyronin Y is localized almost exclusively in mitochondria of cultured cells, similar to another mitochondria! probe, rhodamine 123. At that concentration PY is not toxic but suppressed cell growth, arresting cells[3]. Pyronin Y has long been used, in combination with other dyes such as Methyl Green, as a differential stain for nucleic acids in paraffin tissue sections. In sections stained with Methyl Green-pyronin Y, red blood cells, elastic fibre of blood vessels, zymogen granules of pancreatic acinar cells, surface membrane of heptocytes and kidney tubular cells showed strikingly strong green and/or red fluorescence, while the nuclei of cells appeared non-fluorescent[4]. |
| Cell Assay | The cells are resuspended and stained for 30 min in 1.0 mL of 0.01% pyronin Y in sodiumacetate buffer (1.0 M, pH 4.7). For this purpose 1.0 g of pyronin Y is dissolved in 100 mL distilled water and this solution is purified by chloroform extraction (three fractions of 100 mL). The purified pyronin Y solution is diluted with 1.0 M sodiumacetate buffer pH 4.7 to the appropriate concentration and filtered through paper filters before use. Stained cell samples are studied by fluorescence microscopy (excitation filters SP 560 and LP 515, chromatic beam splitter at 580 nm, barrier filter LP 580) or by flow cytometry[2]. |
| References |
| Melting Point | 250-260ºC(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C17H19ClN2O |
| Molecular Weight | 302.799 |
| Exact Mass | 302.118591 |
| PSA | 19.39000 |
| InChIKey | INCIMLINXXICKS-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| SMILES | CN(C)c1ccc2cc3ccc(=[N+](C)C)cc-3oc2c1.[Cl-] |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water; sparingly soluble in ethanol, ethylene glycol, methyl cellosolve | Soluble in water. Also soluble in methyl cellosolve (9 mg/mL) and ethanol (3 mg/mL). |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xn: Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R68 |
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | BQ1450000 |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
|
~% 
Pyronin Y CAS#:92-32-0 |
| Literature: Australian Journal of Chemistry, , vol. 63, # 4 p. 687 - 692 |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921199090 other acyclic monoamines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Selective growth-inhibitory effect of 8-hydroxyquinoline towards Clostridium difficile and Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum in co-culture analysed by flow cytometry.
J. Med. Microbiol. 63(Pt 12) , 1663-9, (2014) The major risk factor for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is the use of antibiotics owing to the disruption of the equilibrium of the host gut microbiota. To preserve the beneficial resident pro... |
|
|
Evaluation of posterolateral lumbar fusion in sheep using mineral scaffolds seeded with cultured bone marrow cells.
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15(12) , 23359-76, (2014) The objective of this study is to investigate the efficacy of hybrid constructs in comparison to bone grafts (autograft and allograft) for posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF) in sheep, instrumented wit... |
|
|
The orphan nuclear receptor NR4A1 specifies a distinct subpopulation of quiescent myeloid-biased long-term HSCs.
Stem Cells 33(1) , 278-88, (2014) Hematopoiesis is maintained throughout life by self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that differentiate to produce both myeloid and lymphoid cells. The NR4A family of orphan nuclear receptors,... |
|
Name: Luminescence-based cell-based primary high throughput screening assay to identify ago...
Source: The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center
Target: mu-type opioid receptor isoform MOR-1 [Homo sapiens]
External Id: OPRM1-OPRD1_AG_LUMI_1536_1X%ACT PRUN
|
|
Name: QFRET-based biochemical primary high throughput screening assay to identify exosite i...
Source: The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center
Target: disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 17 preproprotein [Homo sapiens]
External Id: ADAM17_INH_QFRET_1536_1X%INH PRUN
|
|
Name: Fluorescence-based cell-based primary high throughput screening assay to identify ago...
Source: The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center
Target: muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 [Homo sapiens]
External Id: CHRM1_AG_FLUO8_1536_1X%ACT PRUN
|
|
Name: uHTS identification of small molecule activators of the adaptive arm of the Unfolded ...
Source: Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics
Target: N/A
External Id: BCCG-A405-UPR-XBP1-PrimaryAgonist-Assay
|
|
Name: Fluorescence polarization to screen for inhibitor that competite the binding of FadD2...
Source: Broad Institute
Target: FATTY-ACID-CoA LIGASE FADD28 (FATTY-ACID-CoA SYNTHETASE)
External Id: 2147-01_Inhibitor_SinglePoint_HTS_Activity
|
|
Name: Bursicon-induced LGR2 mediated cAMP production in LGR-2/CRE6x-Luciferase co-transfect...
Source: Broad Institute
Target: N/A
External Id: Bursicon-induced LGR2 mediated cAMP production in LGR-2/CRE6x-Luciferase co-transfected HEK293 cells Inhibition - 7011-01_Antagonist_SinglePoint_HTS_Activity
|
|
Name: Antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli K-12 3-AG300 harboring AcrB-615-628Me...
Source: ChEMBL
Target: Escherichia coli
External Id: CHEMBL1679886
|
|
Name: Dose response confirmation of uHTS hits for Apaf-1 using a LZ-Caspase-9/Caspase-3 Flu...
Source: Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics
Target: caspase-3 preproprotein [Homo sapiens]
External Id: SBCCG-A720-APAF-1-Inhibitor-Casp9-3-DR-Assay
|
|
Name: Fluorescence-based cell-based primary high throughput screening assay to identify pos...
Source: The Scripps Research Institute Molecular Screening Center
Target: muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 [Homo sapiens]
External Id: CHRM1_PAM_FLUO8_1536_1X%ACT PRUN
|
|
Name: Antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli K-12 3-AG300 harboring AcrB-G616N mut...
Source: ChEMBL
Target: Escherichia coli
External Id: CHEMBL1679880
|
| N-[6-(dimethylamino)-3H-xanthen-3-ylidene]-N-methylmethanaminium chloride |
| Pyronine Y |
| Tetramethyl pyronin |
| EINECS 202-147-8 |
| Ammonium, [6-(dimethylamino)-3H-xanthen-3-ylidene]dimethyl-, chloride |
| N-[6-(Dimethylamino)-3H-xanthene-3-ylidene]-N-methylmethanaminium Chloride |
| Pyronine |
| Methanaminium, N-[6-(dimethylamino)-3H-xanthen-3-ylidene]-N-methyl-, chloride (1:1) |
| Pyroniny(G) |
| Methyl pyronin |
| Pyronin G |
| Pyronine G chloride |
| Pyronine ZH |
| MFCD00011725 |
| [6-(dimethylamino)xanthen-3-ylidene]-dimethylazanium,chloride |
| pyronine G hydrochloride |
| xanthylium, 3,6-bis(dimethylamino)-, chloride (1:1) |
| Xanthylium, 3,6-bis(dimethylamino)-, chloride |
| Pyronin Y |
| 6-(Dimethylamino)-N,N-dimethyl-3H-xanthen-3-iminium chloride |
| Pyronine G |
| Pyronin Yellow |
| 3,6-Bis(dimethylamino)xanthenium chloride |
| [6-(Dimethylamino)-3H-xanthen-3-ylidene]dimethylammonium Chloride |
| tetramethyldiaminoxanthylium chloride |