Rebeccamycin
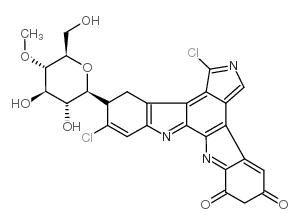
Rebeccamycin structure
|
Common Name | Rebeccamycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 93908-02-2 | Molecular Weight | 570.37800 | |
| Density | 1.87g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C27H21Cl2N3O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of RebeccamycinRebeccamycin, an antitumor antibiotic, inhibits DNA topoisomerase I. Rebeccamycin appears to exert its primary antineoplastic effect by poisoning topoisomerase I and has negligible effect on protein kinase C and topoisomerase II[1][2]. |
| Name | rebeccamycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Rebeccamycin, an antitumor antibiotic, inhibits DNA topoisomerase I. Rebeccamycin appears to exert its primary antineoplastic effect by poisoning topoisomerase I and has negligible effect on protein kinase C and topoisomerase II[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase I Traditional Cytotoxic Agents |
| In Vitro | Rebeccamycin is an antitumor antibiotic produced by the actinomycete Saccharotrix aerocolonigenes with activity against several human tumor cell lines, including A549 (lung adenocarcinoma), HCT-116 (colon carcinoma), and KB (nasopharyngeal carcinoma) [1]. Rebeccamycin shows antibacterial activity against several Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis[3]. |
| In Vivo | Rebeccamycin (2-256 mg/kg; i.p.; daily for 9 days) prolongs survival in B16 melanoma, L1210 leukemia[2]. Animal Model: CDF1 mice (B16 melanoma, L1210 leukemia)[2] Dosage: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256 mg/kg Administration: I.p.; daily for 9 days Result: Prolongation of survival of the mice at dose levels ranging from 8 to 256 mg/kg. |
| References |
| Density | 1.87g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C27H21Cl2N3O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 570.37800 |
| Exact Mass | 569.07600 |
| PSA | 150.37000 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.844 |
| InChIKey | QEHOIJJIZXRMAN-QZQSLCQPSA-N |
| SMILES | COC1C(CO)OC(n2c3c(Cl)cccc3c3c4c(c5c6cccc(Cl)c6[nH]c5c32)C(=O)NC4=O)C(O)C1O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATAMUTATION DATA
|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
~% 
Rebeccamycin CAS#:93908-02-2 |
| Literature: Kaneko; Wong; Okamoto; Clardy Tetrahedron Letters, 1985 , vol. 26, # 34 p. 4015 - 4018 |
|
~% 
Rebeccamycin CAS#:93908-02-2 |
| Literature: Kaneko; Wong; Okamoto; Clardy Tetrahedron Letters, 1985 , vol. 26, # 34 p. 4015 - 4018 |
|
~% 
Rebeccamycin CAS#:93908-02-2 |
| Literature: Kaneko; Wong; Okamoto; Clardy Tetrahedron Letters, 1985 , vol. 26, # 34 p. 4015 - 4018 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
|
Structure and mechanism of the rebeccamycin sugar 4'-O-methyltransferase RebM.
J. Biol. Chem. 283(33) , 22628-36, (2008) The 2.65-angstroms crystal structure of the rebeccamycin 4'-O-methyltransferase RebM in complex with S-adenosyl-l-homocysteine revealed RebM to adopt a typical S-adenosylmethionine-binding fold of sma... |
|
|
Natural product diversification using a non-natural cofactor analogue of S-adenosyl-L-methionine.
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(9) , 2760-1, (2006) Adenosine analogues bearing either 5'-aziridine or 5'-N-mustard electrophiles are methyltransferase-dependent DNA alkylating agents. We present here a novel synthetic cofactor bearing a pendant 5'-ami... |
|
|
Engineering biosynthetic pathways to generate antitumor indolocarbazole derivatives.
J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 33(7) , 560-8, (2006) The indolocarbazole family of natural products is a source of lead compounds with potential therapeutic applications in the treatment of cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Rebeccamycin and stauro... |
| AmbotzLS-1199 |
| MFCD01718312 |
![1,11-dichloro-12,13-dihydro-6-[(phenylmethoxy)methyl]-5H-indolo[2,3-a]pyrrolo[3,4-c]carbazole-5,7(6H)-dione structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/326/102147-53-5.png)
