Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, human
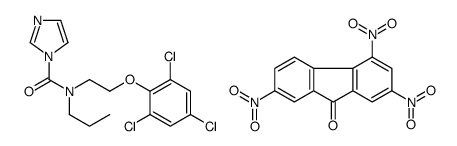
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, human structure
|
Common Name | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, human | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94948-59-1 | Molecular Weight | 691.86000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H21Cl3N6O9 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Name | N-Propyl-N-[2-(2,4,6-trichlorophenoxy)ethyl]-1H-imidazole-1-carbo xamide-2,4,7-trinitro-9H-fluoren-9-one (1:1) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Molecular Formula | C28H21Cl3N6O9 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 691.86000 |
| Exact Mass | 690.04400 |
| PSA | 201.89000 |
| LogP | 8.79460 |
| Storage condition | 20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;half-mask respirator (US);multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| RTECS | MT6435000 |
|
Coordination complexes as molecular glue for immobilization of antibodies on cyclic olefin copolymer surfaces.
Anal. Biochem. 456 , 6-13, (2014) A novel metal-based chelating method has been used to provide an order of magnitude increase in immunoassay performance on cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) plastics compared with passive binding. COCs ar... |
|
|
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 promotes acute cellular and systemic inflammation.
Sci. Signal. 8 , ra86, (2015) Inflammatory critical illness is a syndrome that is characterized by acute inflammation and organ injury, and it is triggered by infections and noninfectious tissue injury, both of which activate inna... |
|
|
A cellular screen identifies ponatinib and pazopanib as inhibitors of necroptosis.
Cell Death Dis. 6 , e1767, (2015) Necroptosis is a form of regulated necrotic cell death mediated by receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) and RIPK3. Necroptotic cell death contributes to the pathophysiology o... |
| MFCD00148692 |