Phytochelatin 2 (PC2)
Modify Date: 2024-01-03 10:41:35
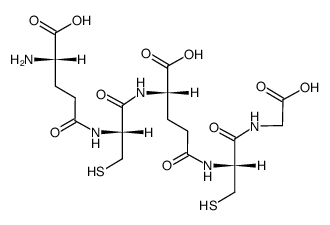
Phytochelatin 2 (PC2) structure
|
Common Name | Phytochelatin 2 (PC2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 95014-75-8 | Molecular Weight | 539.58000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H29N5O10S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Phytochelatin 2 (PC2)Phytochelatin 2, a short phytochelatin, is a key plant peptide binding heavy metals. Phytochelatins are a diverse set of plant compounds that chelate metals, protect against metal toxicity and function in metal homeostasis[1][2]. |
| Name | H-γ-L-Glu-L-Cys-γ-L-Glu-L-Cys-Gly-OH (cadystin B (2)) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Phytochelatin 2, a short phytochelatin, is a key plant peptide binding heavy metals. Phytochelatins are a diverse set of plant compounds that chelate metals, protect against metal toxicity and function in metal homeostasis[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Phytochelatin synthase (PCS) uses the substrates glutathione (GSH, γGlu-Cys-Gly) and a cadmium (Cd)-bound GSH (Cd∙GS2) to produce the shortest phytochelatin product (PC2, (γGlu-Cys)2-Gly) through a ping-pong mechanism[3]. Phytochelatins and their glutathione (GSH) precursor are thiol-rich peptides that play an important role in heavy metal detoxification in plants and microorganisms[4]. |
| References |
[1]. phytochelatin, heavy, metals, chelate, homeostasis, glutathione, microorganisms, toxicity |
| Molecular Formula | C18H29N5O10S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 539.58000 |
| Exact Mass | 539.13600 |
| PSA | 331.92000 |
| PC2 |
| γGlu-Cys-γGlu-Cys-Gly |
| H-(γ-Glu-Cys)2-Gly-OH |
| H-(γ-Glu-Cys)2-Gly-OH |
| (γ-Glu-Cys)2-Gly |
| Cadystin (γEC)2G |

