Erianin
Modify Date: 2024-01-02 09:58:28
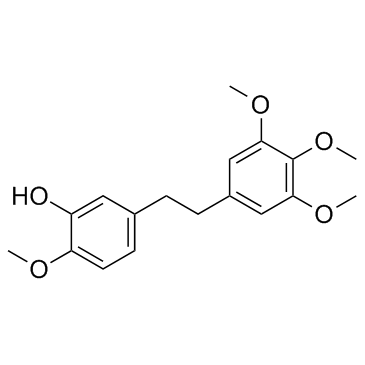
Erianin structure
|
Common Name | Erianin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 95041-90-0 | Molecular Weight | 318.364 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 439.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C18H22O5 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 219.4±27.3 °C | |
Use of ErianinErianin, often used as an antipyretic and analgesic agent, could inhibit IDO-induced tumor angiogenesis. |
| Name | 2-methoxy-5-[2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]phenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Erianin, often used as an antipyretic and analgesic agent, could inhibit IDO-induced tumor angiogenesis. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Erianin is often used as antipyretic and analgesic agent. Erianin belongs to bibenzyl derivatives in structure, with the activity of anti-virus, anti-bacterial, as well as anti-benign prostatic hyperplasia. Erianin has obvious damage on 2LL-IDO cells, Erianin basically has no cytotoxicity on human normal liver cell line L02, and cell viability is maintained at around 85%[1]. Erianin inhibits the growth of HeLa cells and induces apoptosis in a dose‑ and time‑dependent manner, inducing cell cycle arrest at the G2/M stage. Erianin treatment also increases the expression of Bax and caspase‑3, but decreases levels of Bcl‑2 and phosphorylated‑ERK1/2[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 439.1±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H22O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 318.364 |
| Flash Point | 219.4±27.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 318.146729 |
| PSA | 57.15000 |
| LogP | 3.11 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.554 |
| Phenol, 2-methoxy-5-[2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]- |
| Dihydrocombretatastin A-4 |
| Erianin |
| 2-methoxy-5-[2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-ethyl]-phenol |
| 5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethyl)-2-methoxyphenol |
| 2-Methoxy-5-[2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]phenol |
| (E)-2-methoxy-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylethyl)phenol |
| 3-hydroxy-3',4',4,5'-tetramethoxybibenzyl |
| 2-Methoxy-5-[2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethyl]benzolol |
![2-methoxy-5-[2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenol Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/240/117048-62-1.png) CAS#:117048-62-1
CAS#:117048-62-1 CAS#:3840-31-1
CAS#:3840-31-1 CAS#:80192-89-8
CAS#:80192-89-8 CAS#:847063-26-7
CAS#:847063-26-7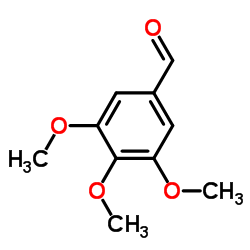 CAS#:86-81-7
CAS#:86-81-7![[3-[(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)oxy]-4-methoxybenzyl]triphenylphosphonium bromide Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/311/121042-94-2.png) CAS#:121042-94-2
CAS#:121042-94-2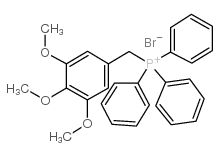 CAS#:61240-20-8
CAS#:61240-20-8
